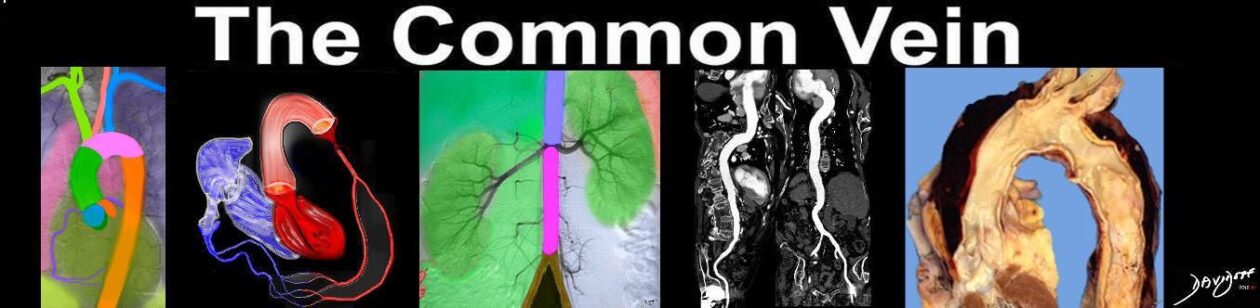
Tubular Portion of the Ascending Aorta
Copyright 2007
The ascending aorta is the most proximal portion of the aorta, starting at the base of the heart and ending at the first brachiocephalic artery at the origin of the aortic arch.The tubular portion starts at the sinotubular junction and extends to the brachiocephalic artery.
Ascending Aorta Bulbous Portion and Tubular Portion |
| 35324b02 Courtesy of Laura Feldman MD |
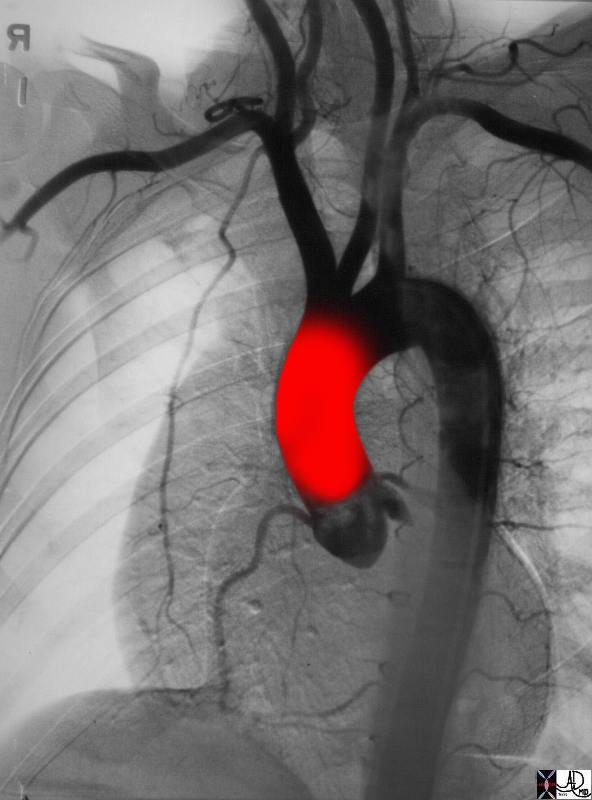
Aortic Bulb Sinotubular Junction, and Tubular Components of the Ascending Aorta |
|
The volume rendered CT scan shows a ridge at the sinotubular junction after which the proximal tubular portion is noted. 47823 Davidoff MD |
Size
It is about 5 cm. in length, extending from the upper part of the base of the left ventricle to the aortic arch. The diameter of the ascending aorta is 3-3.5cms. In young males the ascending aorta measures approximately 35 mm and the descending aorta 25 mm. The size in young females is slightly less. The ascending aorta and the MPA should be about the same size. The A-P dimension of the left atrium should be about the same size as the aortic valve and the LA is just slightly larger than the ascending aorta. The ratio of ascending to descending aorta should normally be about 3:2. Over 55 the descending aorta enlarges (at about 1mm per year) to greater degree than the ascending aorta and thus this ratio changes. Women have slightly smaller aortas than men, even at the same body surface area. The main pulmonary artery is a useful standard axial landmark for measuring the ascending aorta. The measurement is usually made in the transverse plane (perpendicular to the long axis) and at a position where the cut is a transverse.
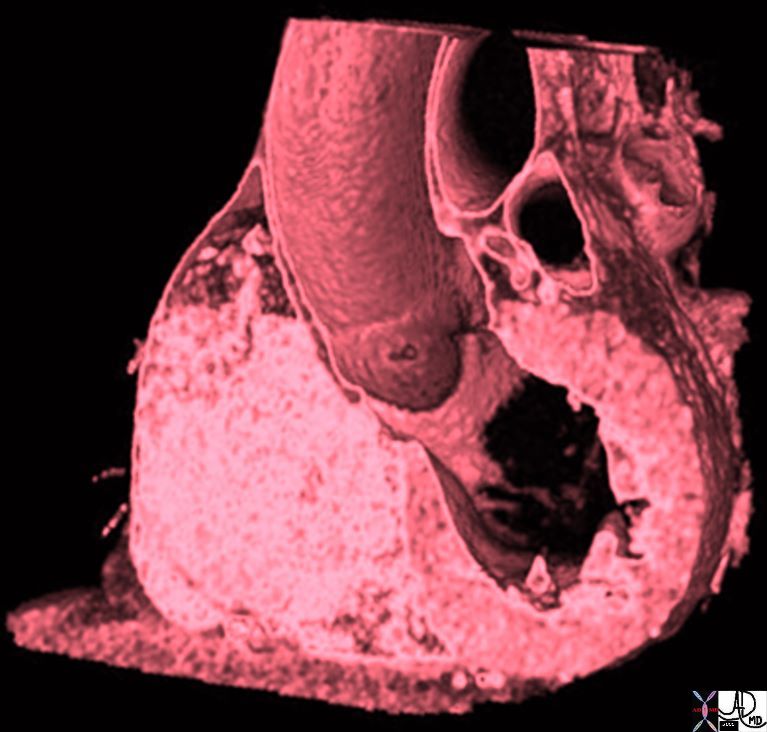
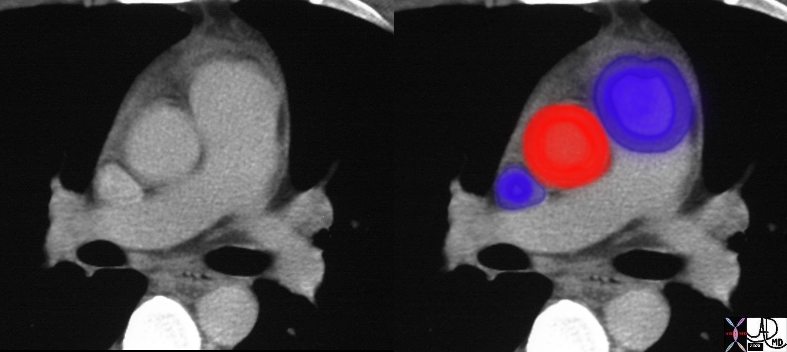
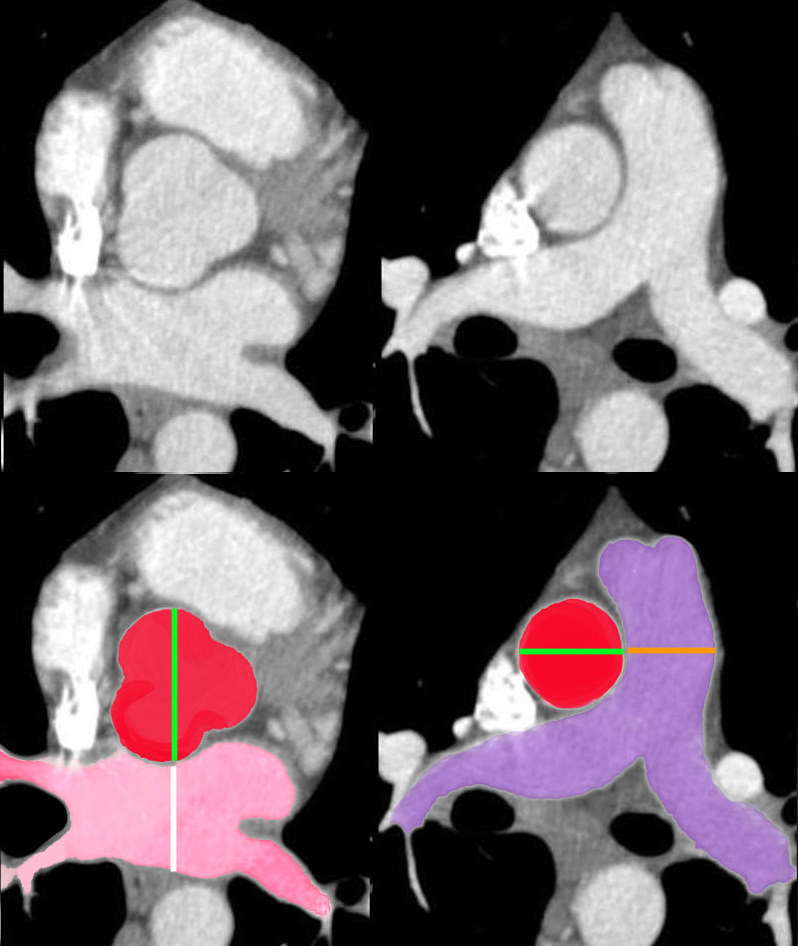 Aorta to Pulmonary Artery Ratio Sinus Portion and Tubular Portion Aorta to Pulmonary Artery Ratio Sinus Portion and Tubular Portion |
| In the first set of images, the aorta at aortic valve level (three red sinuses) is about the same size as the left atrium,(pink) while the ascending aorta (red) is about the same size as the main pulmonary artery (blue purple) in the second set.
34769c07b02 Davidoff MD |
Shape
The ascending aorta is tubular as its name implies, and it curves gently from the sinotubular junction to the right, reaches almost to the lateral edge of the mediastinum and the curves back to join the beginning of the arch.
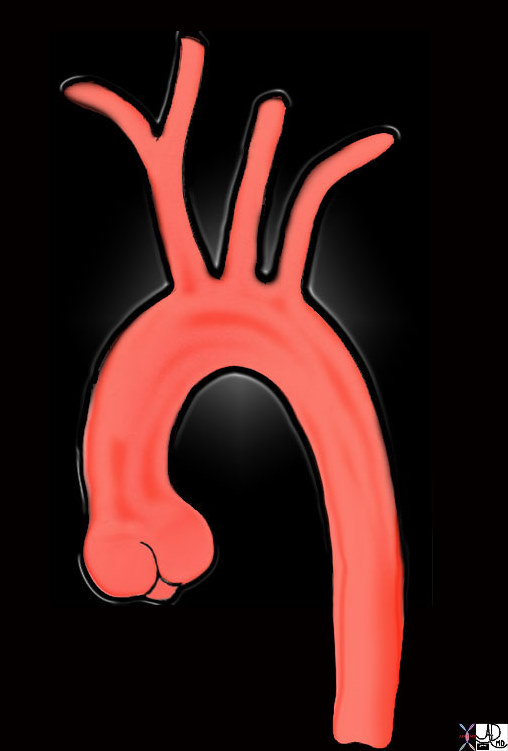
The aorta originates at the base of the heart at the aortic valve, and then it ascends toward the right with a gentle curve that takes the tubular portion back toward the aortic arch. keywords aorta aortic valve sinotubular junction ascending aorta aortic arch brachiocephalic artery left common carotid artery left subclavian artery descending aorta normal TCV Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 47676
Position and Relations
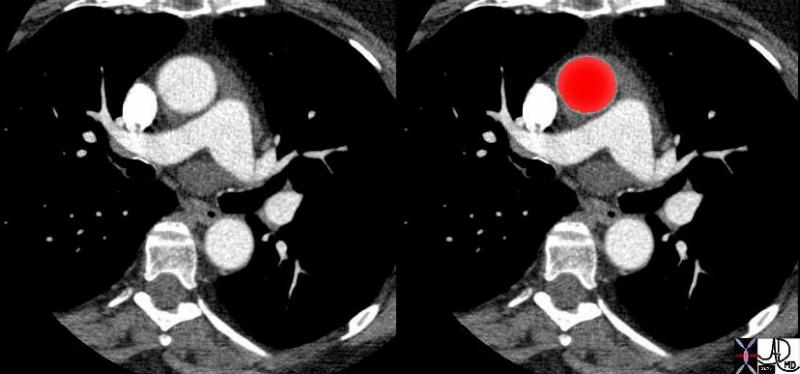
The ascending aorta is located behind the left half of the sternum, and it passes upward, forward, and to the right, forming a slight curve. Lies posterior to rt of main pulmonary artery and anterior and to left of super vena cava
Aorta and Pulmonary Artery – Normal Size and Position |
| 27467c01 aorta pulmonary valve pulmonary artery SVC size position normal CTscan Davidoff MD |
Covering
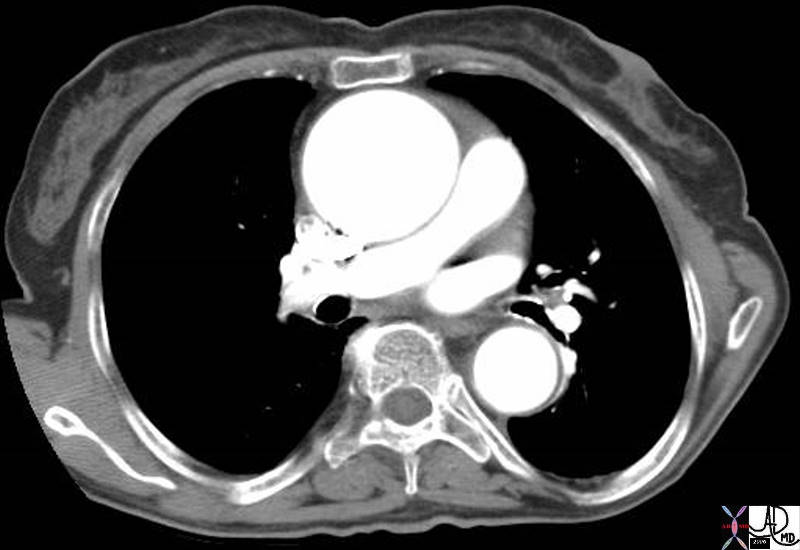
The ascending aorta is covered almost entirely by visceral pericardium.
keywords thorax chest thoracic aorta ascending aorta pericardium pericardial attachment descending aorta size normal relations anatomy shape CTscan
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 39103c01
Applied Biology
Disorders of Size
Aneurysm of the Ascending Aorta
Enlargement caused buy Monkeberg’s Marfans atherosclerosis syphilis result potential to rupture dx echo CT MRI aortography Rx surgical at ??? size
Ascending Aneurysm |
| 42358.800 aorta fx enlarged MPA pulmonary artery aneurysm of the ascending aorta CTscan Davidoff MD |
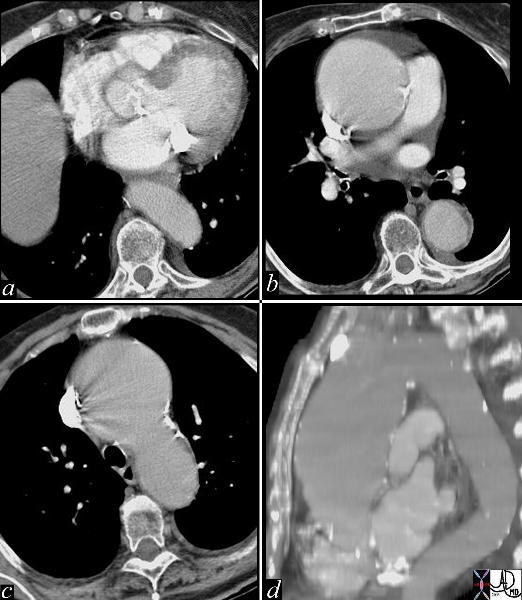
Ascending Aortic Aneurysm |
| This series of images are from a CTscan showing an ascending aortic thoracic aneurysm. There is evidence of heavy calcification of the aortic valve (aortic sclerosis), an aneurysm confined to the ascending aorta (b,c,d), and tortuosity of the descending aorta (d). The cause for the aneurysm is probably a combination of systemic hypertension, aortic stenosis and atherosclerotic degeneration of the wall. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 19426c code CVS thorax aorta ascending aneurysm MAC aortic sclerosis CTscan |
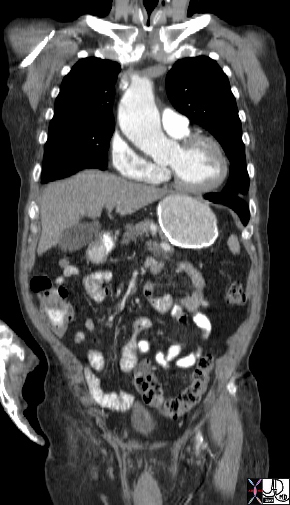
Loss of Tubular Shape |
| 44497 hx 80M thoracic aorta ascending aorta 5.7cms descending aorta 3.5 cms dx enlarged dx aneurysm CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
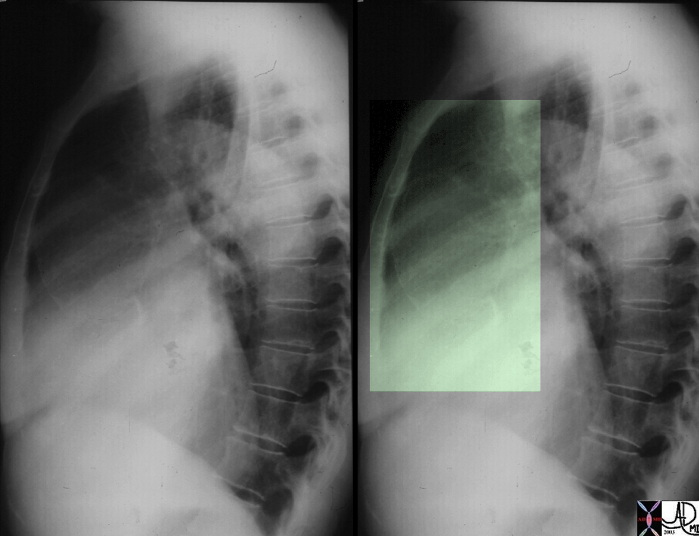
Ascending Aorta – Syphilitic Aortitis – Dilated and Calcified |
| This lateral examination of the chest shows fine calcification in an ectatic ascending aorta associated with aortic annular calcification. Note the remarkable paucity of atherosclerotic change in the descending aorta. These findings are highly characteristic of tertiary syphilis of the aorta. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 00018c code CVS artery aorta ascending syphilis aneurysm calcification tortoise shell |
Disease at the Sinotubular Junction
Supravalvar Aortic Stenosis – William’s Syndrome
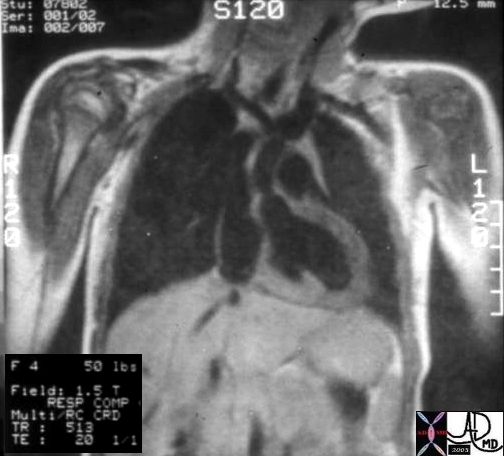
Hx 4 year female with cocktail personality and Williams Syndrome showing supravalvar aortic stenosis
keywords heart cardiac artery aorta supravalvular aortic stenosis supravalvar aortic stenosis Williams syndrome William’s syndrome
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 08233b01
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
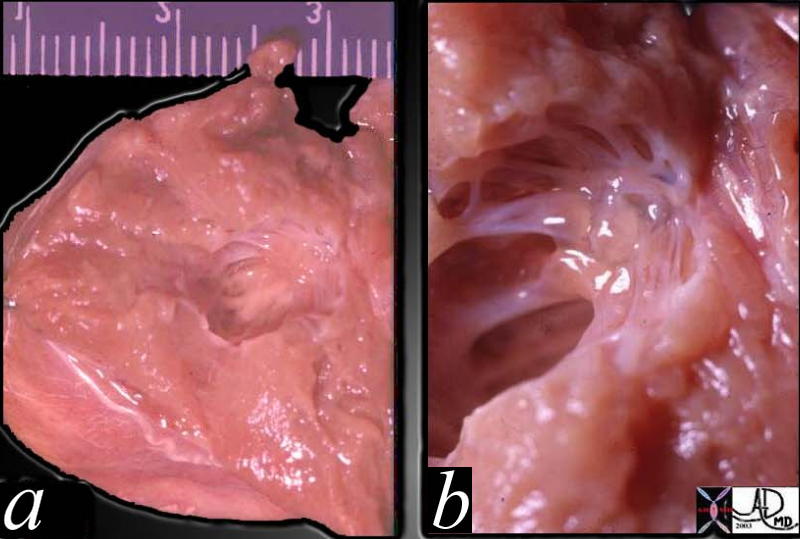
This pathological specimen is from a patient with hypoplastic left heart syndrome, (HLHS) (a) show a diminutive LV cavity (about 5mm in diameter)and MV elements with a relatively thick LV wall. (about 9mms in diameter) Both these findings are characteristic of the disease. a close-up of the MV (b)shows an atretic MV with unformed and poorly formed elements including the chordae and papillary muscles. No lumen could be identified.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net 01813c01
keywords heart cardiac congenital gross pathology HLHS MV cavity LV wall mitral atresia
Congenital caused unknown result poor supply tosystemic circulation dx echo CT MRI aortography Rx Norwood
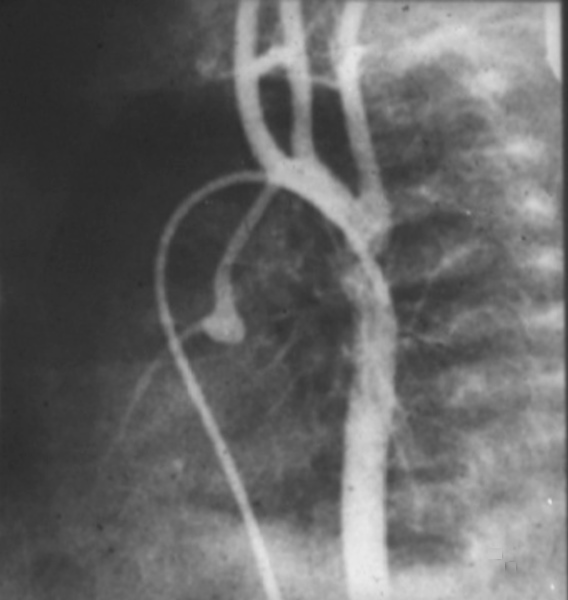
Aortic Valve Atresia in the Setting of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome |
| 00269b02 heart cardiac coronary artery aorta small dx aortic atresia tubular hypoplasia aortic coarctation aortic atresia PDA patent ductus arteriosus angiogram angiogaphy CHD congenital heart disease Davidoff MD 00269b01 00269b02 00269b03 |
Ascending Aortic Dissection
caused unknown aka type A dissection result potential to rupture into pericardium occlude the right cor artery and cause aortic regurgitation – fartal consequencedx CT MRI aortography transesophageal echo Rx Surgical =/- AVR
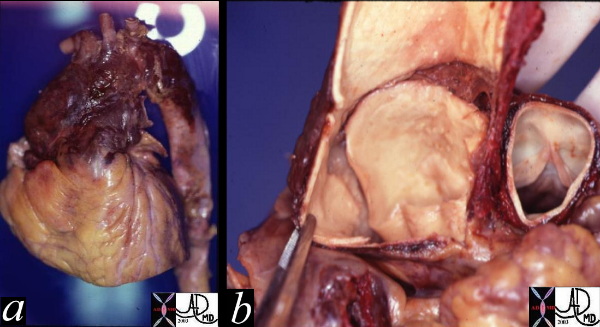
Ascending Aortic Dissection |
| These two pathological specimens show a ruptured dissection isolated to the ascending aorta. The external view (a) shows hemorrhagic change surrounding the ascending aorta with blood tracking into and through the adventitia. Image b, shows the internal intimal tear which in this case is almost circumferential. The dissection only involved the ascending aorta and it was therefore classified as type II in the deBakey system and type A in the Stanford system. Courtesy Henri Cuenoud MD. 13413c code CVS aorta ascending thorax dissection rupture grosspathology |
Ruptured Dissection of the Tubular Portion |
| hx 81F presents with acute shearing back pain and hypotension thorax thoracic aorta ascending aorta fx focal dissection rupture pericardium mediastinum fluid blood pericardial effusion hemopericardium azygous vein fx reflux dx aortic dissection with pericardial tamponade imaging radiology CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 22343bduos500 |
Traumatic Injury
More common at ligamentum caused decelerating trauma eg MVA steering wheel result potential to rupture – fatal dx CT aortography transesophageal echo Rx Surgical Emergency
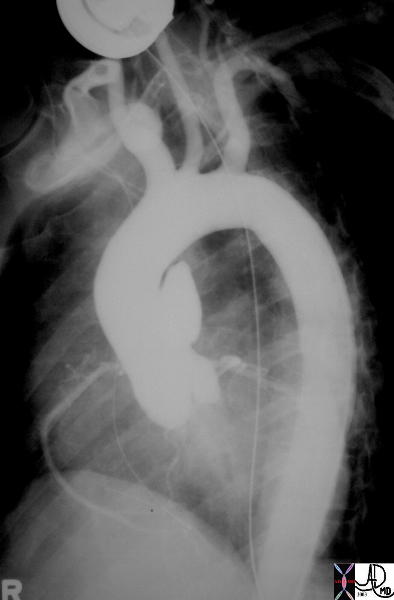
Traumatic Injury to the Ascending Aorta |
| 35290 Courtesy of Laura Feldman MD. code aneurysm aorta artery pseudoaneurysm thorax trauma |