Aortic Trauma
The Common Vein Copyright 2007
Ashley Davidoff MD
Definition
Aortic trauma is usually caused by blunt decelerating injury such as occurs in a motor vehicle accident where the driver or passenger is thrown against a hard part of the car and as the isthmus is anchored by the ligamentum arteriosum, which is therefore held fixed as the deceleration caused by the impact results in a traumatic shear stress on the aorta.
The result may be a tearing, or laceration of the aorta commonly at the isthmus, but it can affect any part of the aorta. The laceration of the aorta which is characteristically a transverse tear usually originating at the insertion point of the ligamentum arteriosum (80%) on inferior surface of the transverse arch. Other sites that sometimes are involved are the proximal ascending aorta and descending aorta at diaphragmatic hiatus.
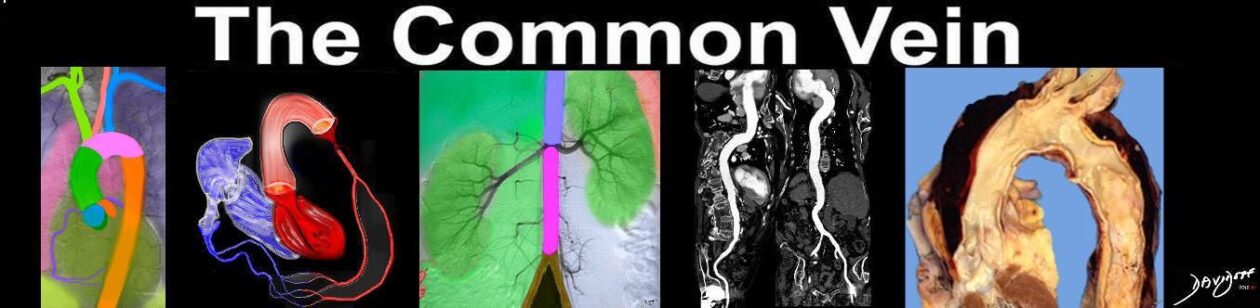
The ligamentum arteriosum is located at the aortic isthmus, where the fixed fibrous ligamentum arteriosum acts as an anchor and puts extra stress on the aorta as it is flung along the line of force. As the patients body is reflected off a hard object the combination of the decelerating force and anchoring forces create a shearing and tearing stress on the isthmus. Many patients die at the scene of the accident as a result of a ruptured aorta. Some patients develop a pseudoaneurysm where the rupture is contained by a combination of remnants of the wall, hematoma and surrounding tissues.
47680 right ventricle heart cardiac right ventricular outflow tract ligamentum arteriosum ductus arteriosus aorta isthmus Davidoff art Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Diagnosis
No specific symptoms or signs reflect this injury and further investigation by CT scan is warranted based solely on high clinical suspicion. Angiography is also an excellent method and is specific and sensitive.
Treatment is emergency surgery.
Diagnosis
No specific symptoms or signs reflect this injury and further investigation by CT scan is warranted based solely on high clinical suspicion.
CXR
Widened mediastinum: Definition: A mediastinum measurement of ≥8 cm or >1/3rd the
transthoracic distance at the level of the aortic knob on a supine AP film.
GUIDELINES:
1. Initially assume that there is an aortic injury on every patient with a rapid deceleration
mechanism of injury.
CXR
a. Pleural cap.
b. Depressed left mainstem bronchus.
c. Trachea or esophagus deviated to right.
d. First and second rib fracture.
e. Obliterated aorto-pulmonary window.
- This grading system is based on anatomical layers of the aortic wall—
- intimal tear (grade I),
- intramural hematoma (grade II),
- pseudoaneurysm (grade III),
- rupture (grade IV)—and directly influences the management of blunt aortic injuries.
Treatment is emergency surgery.
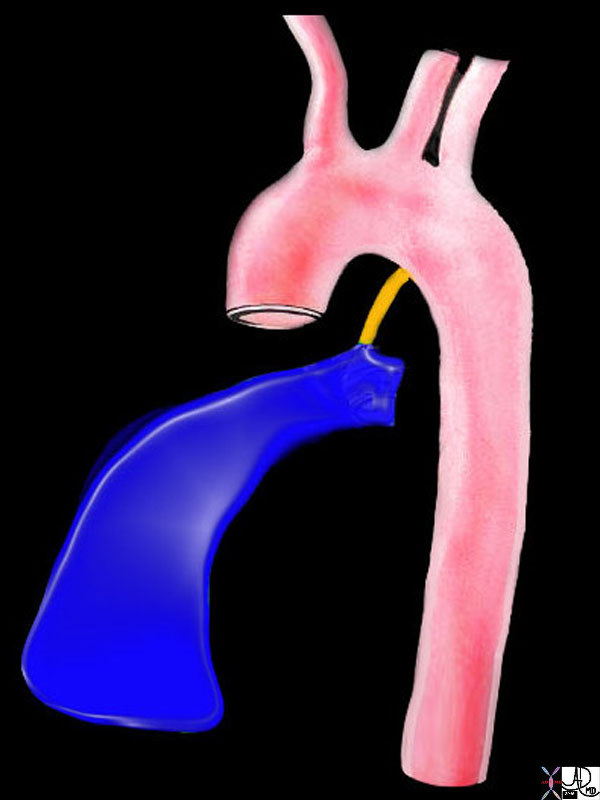
thorax thoracic aorta isthmus aortic laceration pseudoaneurysm leak contained rupture posterior mediastinal hematoma pleura pleural effusion hemothorax aortic laceration trauma traumatic tear trauma MVA CTscan Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 17540c02
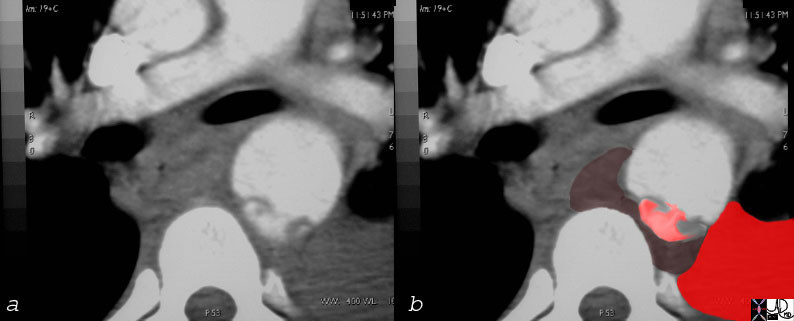
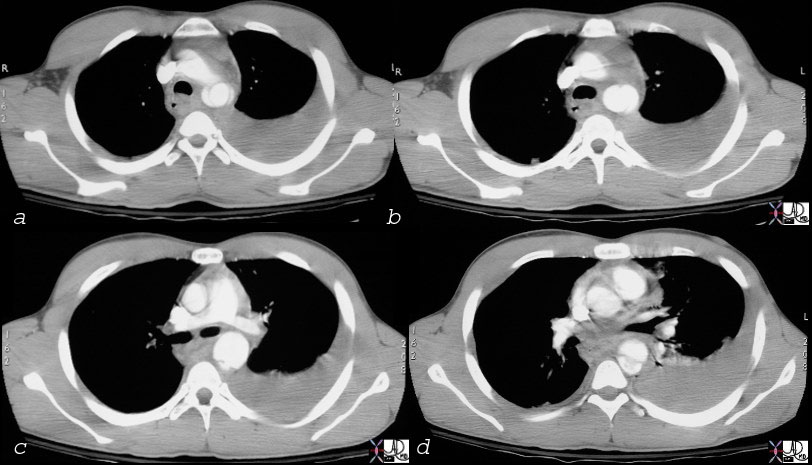
Overlay in red shows the site of the aortic laceration
keywords thorax thoracic aorta isthmus aortic laceration pseudoaneurysm leak contained rupture posterior mediastinal hematoma pleura pleural effusion hemothorax aortic laceration trauma traumatic tear trauma MVA CTscan
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
17540c01
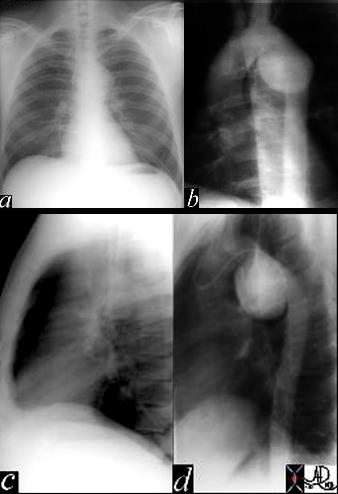
This image represents a combination of plain film CXR and the correlative thoracic aortogram in a 38 year old patient, 13 years after an MVA. There is an aneurysmal bulge at the level of the isthmus, representing a traumatic aneurysm at the characteristic location of the ligamentum arteriosum. The P-A and lateral chest X-ray shows an enlarged and unusually shaped aortic knob and the angiogram confirms the pseudoaneurysm of the aorta. 35178c Courtesy of Laura Feldman MD. TheCommonVein.net
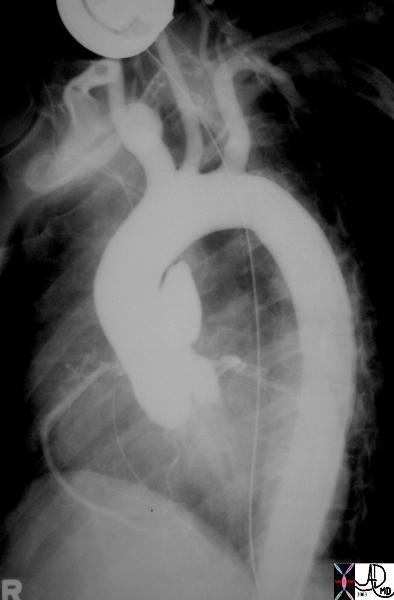
35290
Keywords aneurysm aorta artery pseudoaneurysm thorax trauma
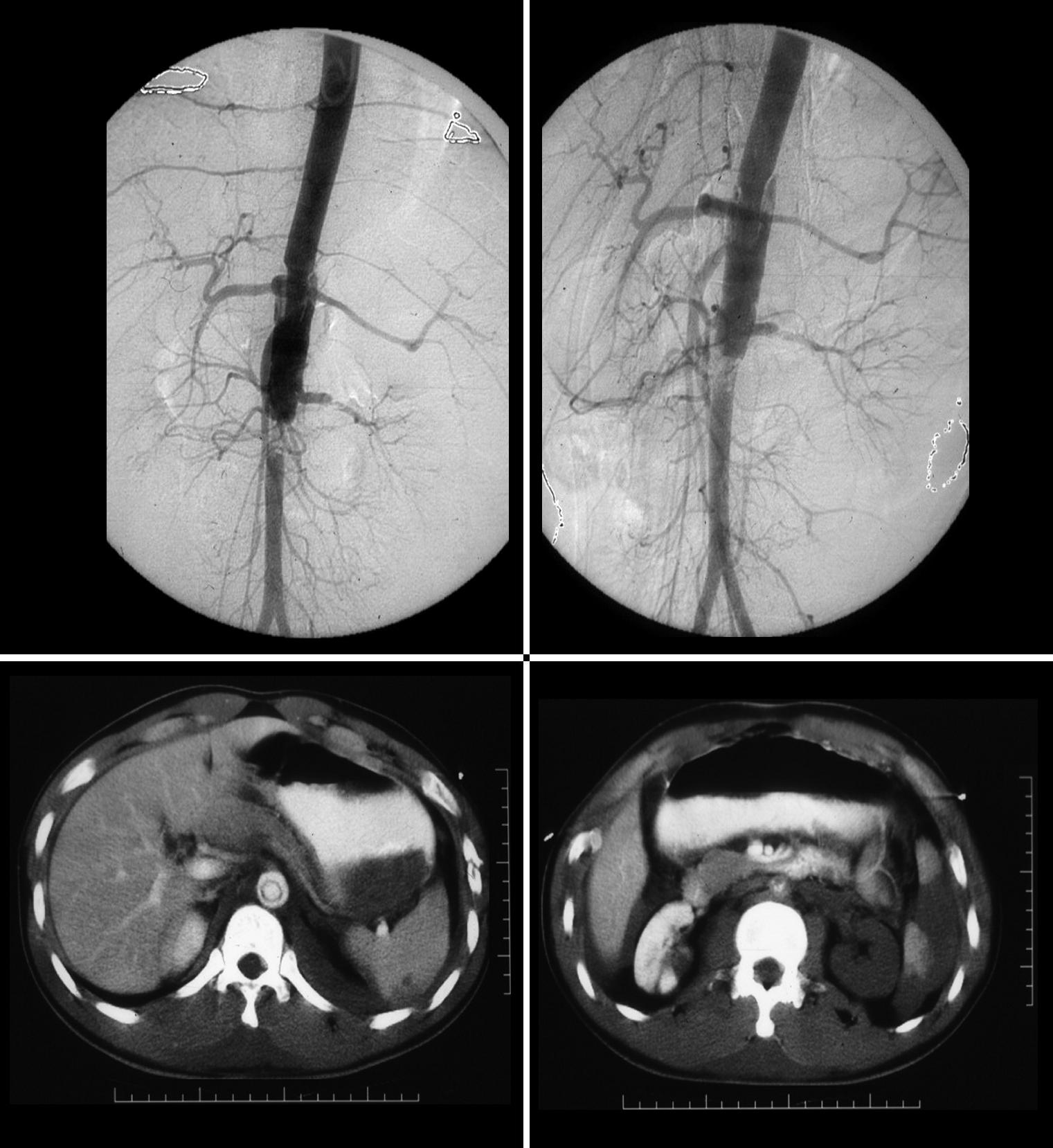
These images represent a traumatic dissection of the abdominal aorta caused by a compression injury to the abdomen. The angiograms in a and b shows what appears to be a complex tear of the aorta with a dissection and then a subtotal obstruction of the aorta distally. The CTscan shows (c) the dissection to better effect, with a subtotal narrowing of the aorta distally. Note also the injury of the left renal artery on the angiogram as well as the lack of perfusion of the left kidney on the CT scan.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. TheCommonVein.net
14734c code aorta abdomen trauma dissection
76 year old female with incidental finding of a traumatic pseudoaneurysm
Axial Plain
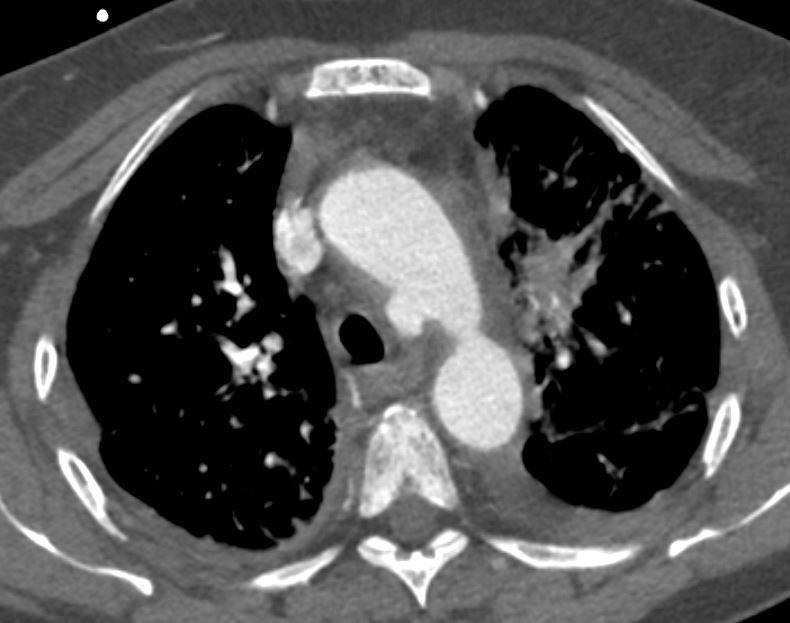
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
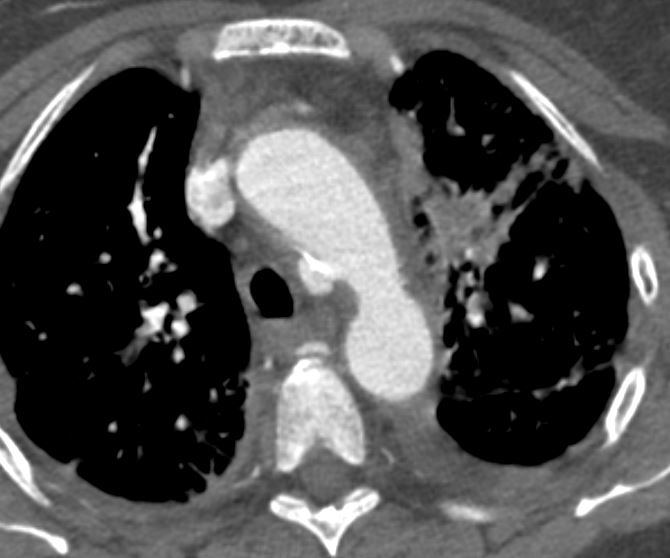
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
Coronal Plane
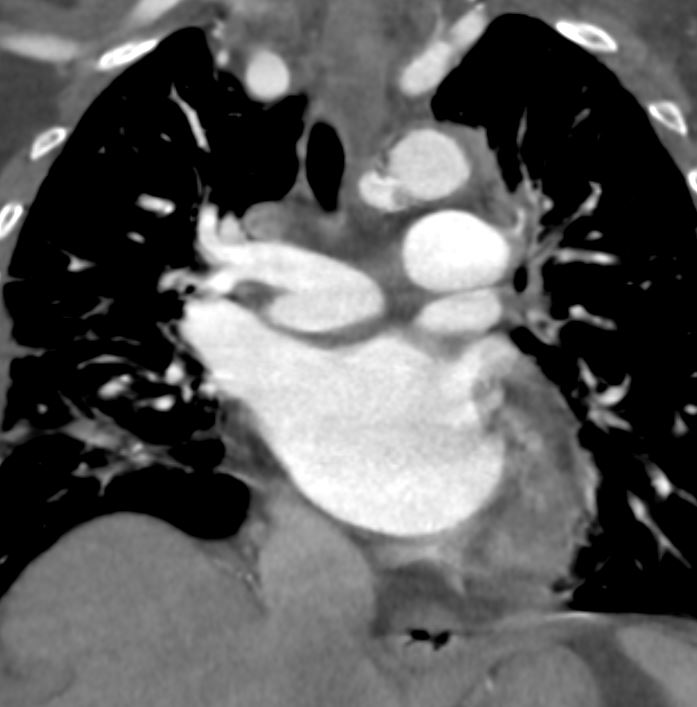
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
References