|
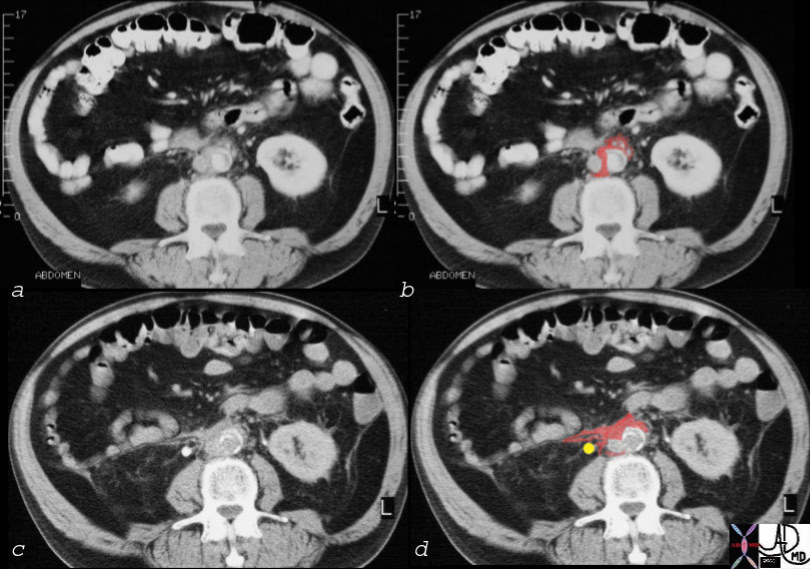
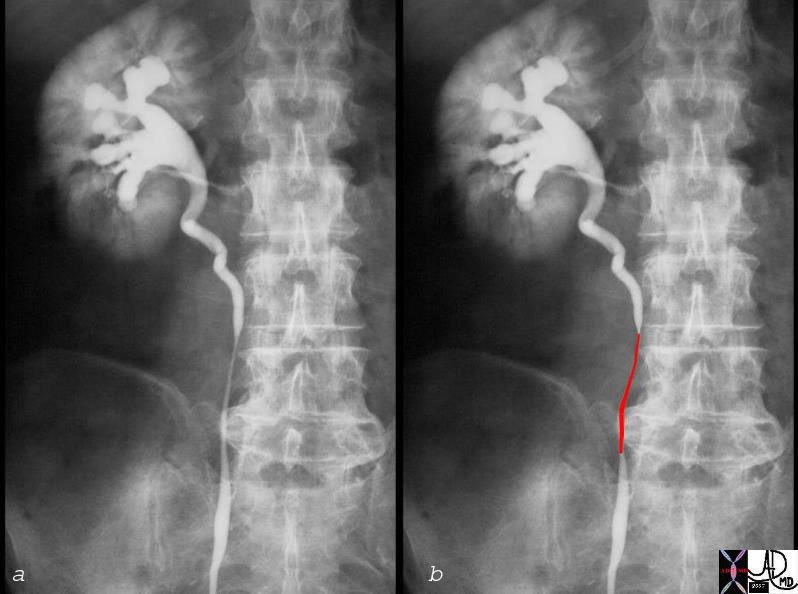
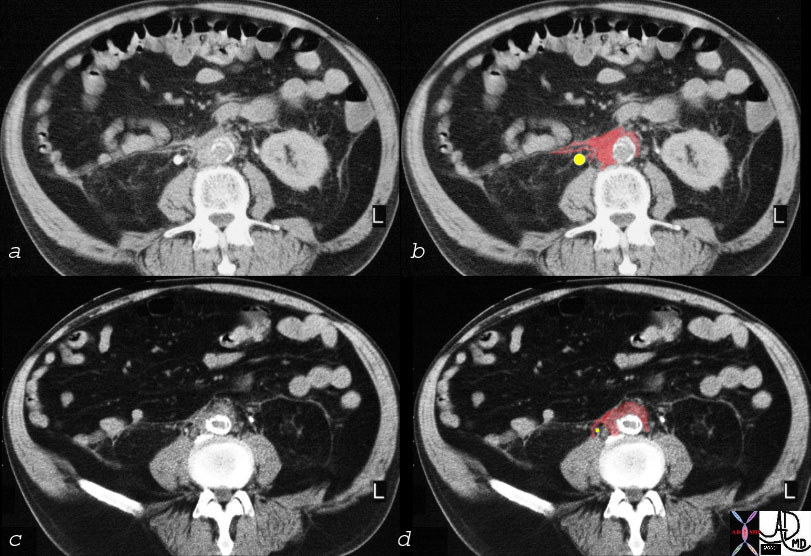
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Copyright 2008 Definition Retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF) is a fibrogenic inflammatory process of the connective tissue of the retroperitoneum that has acute, subacute and chronic manifestations. The cause of the disease in most cases is unknown, but it seems to be commonly associated with atherosclerosis. It has been suggested that it is an autoimmune response to a lipid that originates from the atherosclerotic process arising in the wall of the aorta. The lipid is known as ceroid. Other associated causes include inflammatory diseases such as post irradiation, drugs (methysergide chemotherapy) retroperitoneal infection or malignancy. The result is progressive fibrosis of retroperitoneal connective tissue, with the dominant result being the stenosis and subsequent obstruction of the ureters.
Treatment options include surgical release. The use of steroids is controversial.
References |