GCA is a systemic granulomatous vasculitis involving
- most commonly involving the external carotid branches,
- especially the superior temporal artery
- cranial arteries
- vertebral arteries
- coronary arteries
- mesenteric arteries
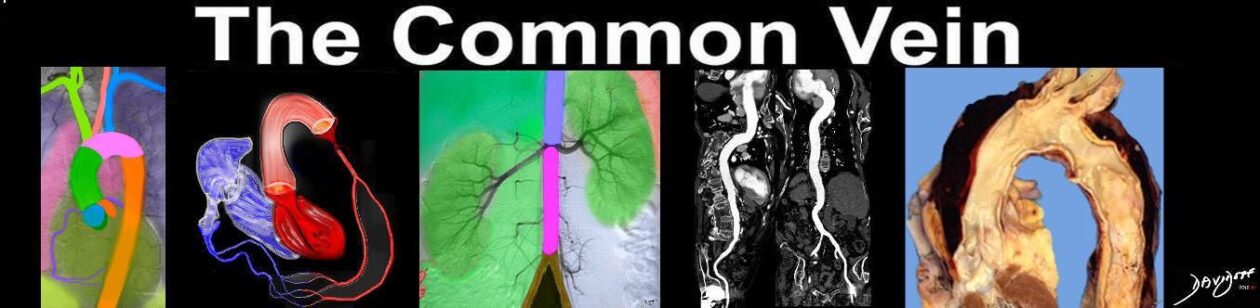
- aorta 15%
- annuloaortic ectasia or
- ascending aortic aneurysm that can extend into the aortic arch
- acute dissection, aortic valve insufficiency, or abdominal aortic aneurysm
- most common form of aortitis in North America, accounting for more than 75% of cases
Etiology
PF >50
Result
-
- acute phase – destruction of the internal elastic lamina
- inflammatory cellular infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells and lymphocytes
- Chronic – fibrosis of the wall
- acute phase – destruction of the internal elastic lamina

Radiographics Restrepo 2011
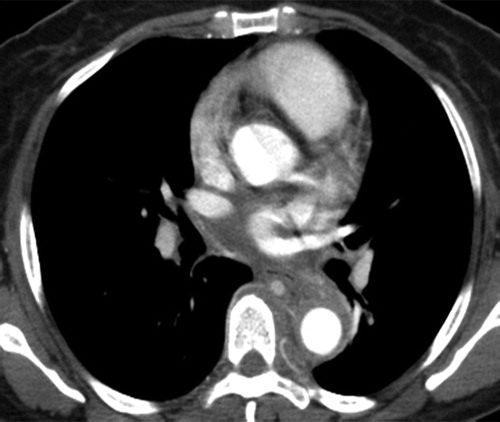
Radiographics Restrepo 2011
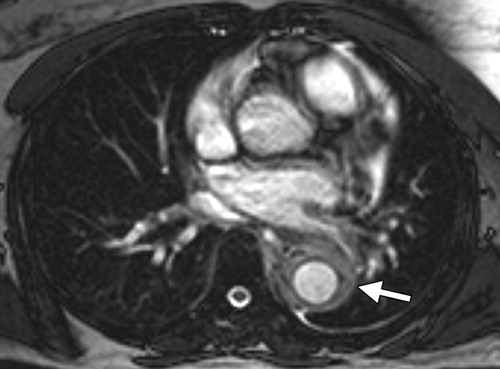
Radiographics Restrepo 2011
Radiographics Restrepo 2011