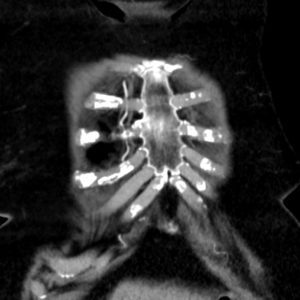
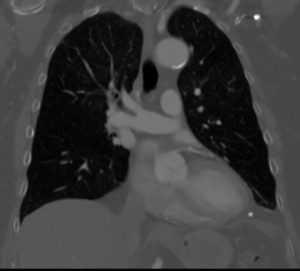
Coarctation of the Aorta
Copyright 2008
Definition
Coarctation of the aorta is a relatively common congenital disorder of the aorta and it is characterized
by a focal narrowing usually at the level of the isthmus. It accounts for 5-8% of disorders.
The cause is unknown, but there is a known genetic association with 30% of siblings known to have the abnormality. Associated defects include VSD and PDA. 65-70% of the patients have a bicuspid aortic valve. The structural defect consists of thickening of the media, or may appear as a membrane that occurs in a juxtaductal location. It is sometimes only a focal ring like stenosis, and on other occasions it a longer segment may be involved. Occasionally it is present in the more distal thoracic aorta whule the abdominal aorta is rarely involved.
The abnormality results in high upstream pressure, and low downstream pressure and is compensated for by associated left ventricular hypertrophy and numerous collaterals of the internal mammary and intercostal vessels.
The diagnosis is suspected clinically when the upper limb pulse and pressures are higher than the lower limb findings. Echocardiography is the study of choice both in the diagnosis of the structural defect as well as the assessment of the gradient. CTA and MRA are excellent alternatives.
Treatment options include balloon angioplasty and open surgical repair.
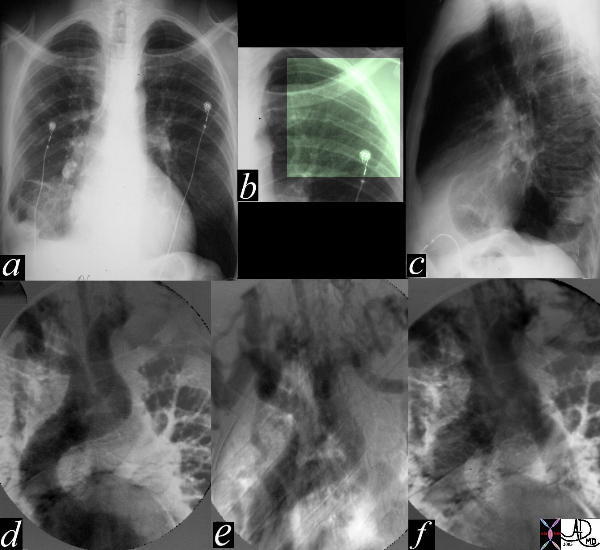
Severe Coarctation Plain Film and Angiography |
| The most obvious finding in this CXR (a) with pleuro-parenchymal changes is not the most significant. In image (b) the highlighted ribs reveal rib notching characteristic of coarctation of the aorta. The lateral examination (c) in this instance is not helpful. In the early phase of the angiogram(d), there appears to be complete interruption of the aorta with a large left subclavian artery acting as a collateral pathway. The sbsequent images e, and f, show progressive filling of the isthmus and distal thoracic aorta. The coarcatation becomes apparent characterised by a “3” sign. 35107c Courtesy Laura Feldman MD code CVS artery aorta thorax coarctation rib notching bone collateral |
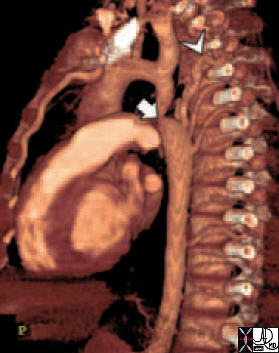
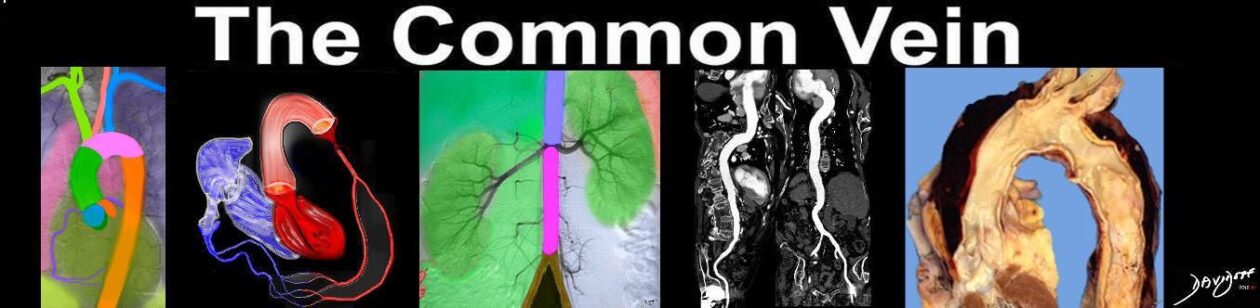
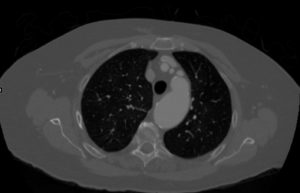
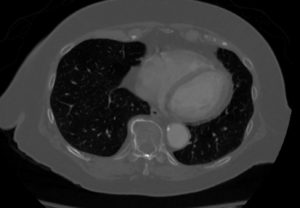
CTA with 3D reconstruction |
| 44146 coarctation of the aorta heart cardiac CTscan MDCT Courtesy Philips Medical |
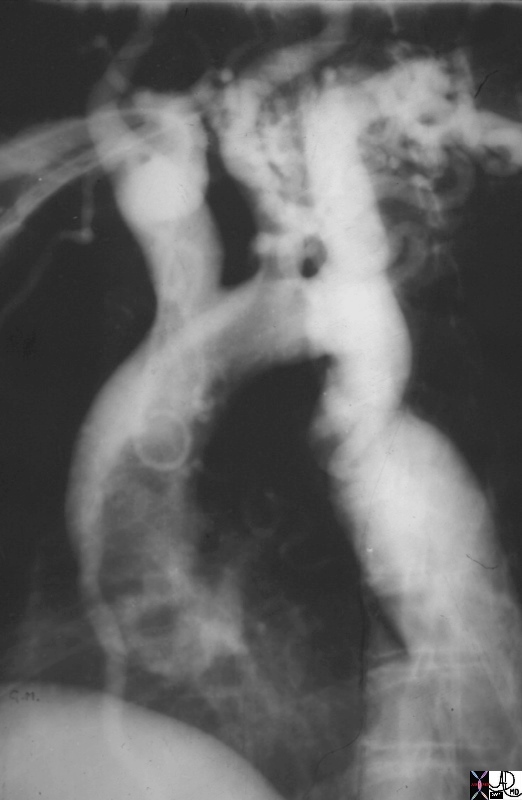
Juxtaductal Coartctation with Mild Arch Hypoplasia, and a Large Internal Mammary Collateral Vessel |
| 00253.800 19 year old male aorta thorax thoracic aorta isthmus post ductal coarctation of the aorta 3 sign three sign collateral enlarged internal mammary artery angiogram angiography aortogram aortography Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
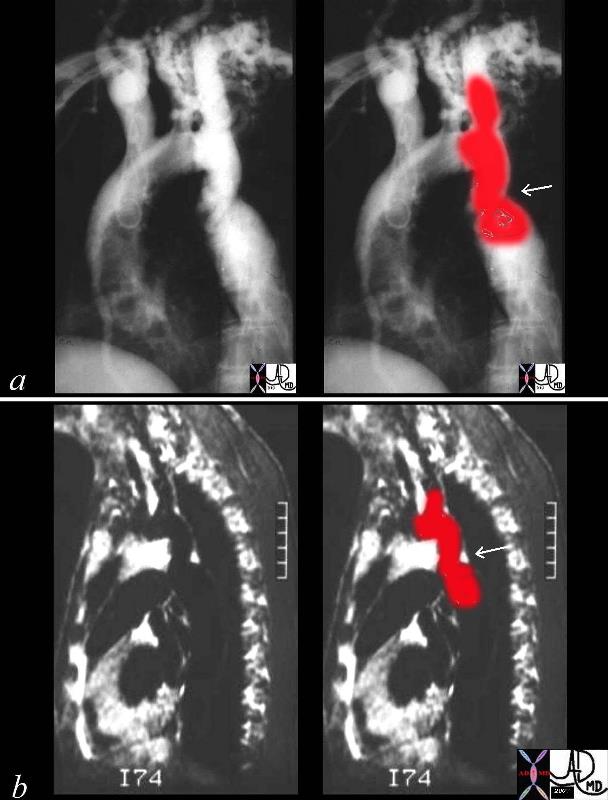
Coartcation of the Aorta |
| 00254c04 This combination of an angiogram and MRI show a focal coarctation of the aorta distal to the dilated left subclavian artery. Note the large internal mammary artery in the angiogram (a) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 00254c02 CVS aorta thorax thoracic aorta coarctation |
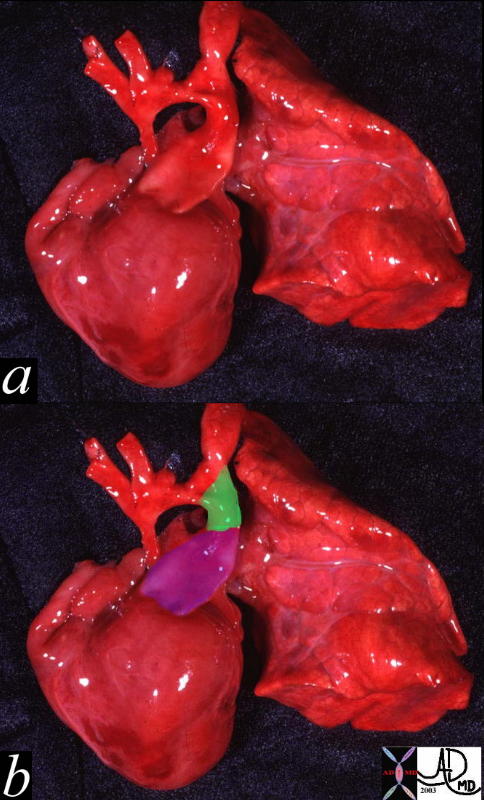
Hypoplastic Aorta Involving the Ascending Arcg, and juxtaductal components A PDA is present (green) |
| This pathologic specimen shows a small ascending aorta, and arch with a diffuse coarctation. with a large pulmonary artery (purple overlay in b) and a patent ductus arteriosus (green overlay in b)Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 00264c code heart cardiac hypoplastic aortic arch PDA coarctation of the aorta AO congenital grosspathology |