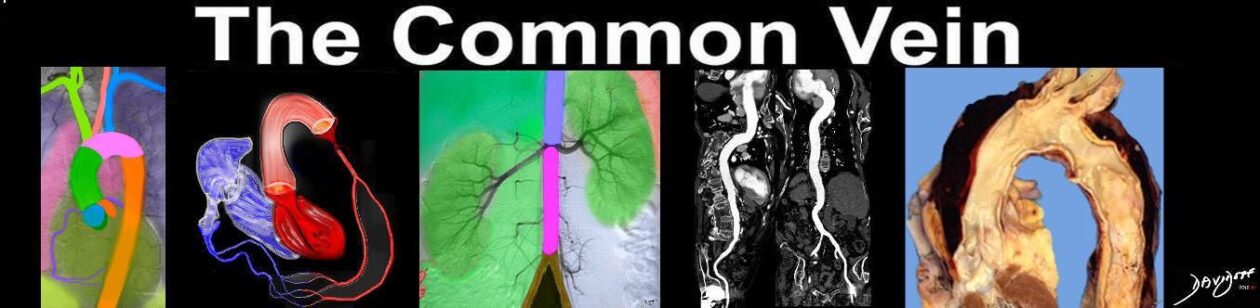
Aortitis is abnormal inflammation of the aortic wall
Caused by a broad category of infectious or noninfectious conditions in which there
- Noninfectious aortitis occurs in large-vessel vasculitides
- Takayasu arteritis
- giant cell arteritis (GCA).
- rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE
- ankylosing spondylitis.
- reiters
- Infectious aortitis may be secondary to
- tuberculosis,
- syphilis,
- Salmonella or other bacterial or viral pathogens.
Clinical nonspecific and may include pain, fever
Diagnosis Imaging
magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, MR angiography, and computed tomographic angiography
noninfectious (more common)
Takayasu arteritis and giant cell arteritis (GCA). It is also seen in other collagen vascular disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
infectious
tuberculosis, syphilis, or infection with Salmonella or other bacterial or viral pathogens.

Rebello et al Radiographics
CT angiography has excellent spatial resolution and is commonly the initial imaging study (gated)
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is recommended for serial imaging
Nuclear medicine imaging with fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) or gallium 67 (67Ga) is helpful in assessment of inflammatory activity

Radiographics Restrepo 2011
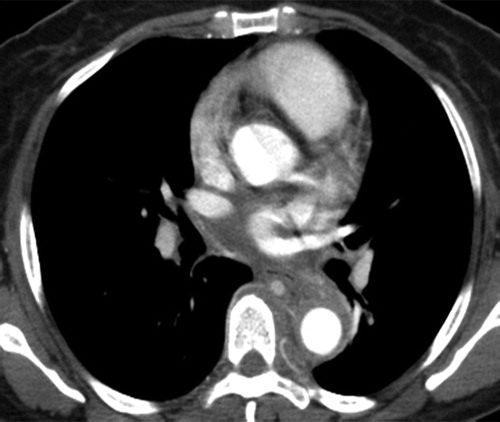
Radiographics Restrepo 2011
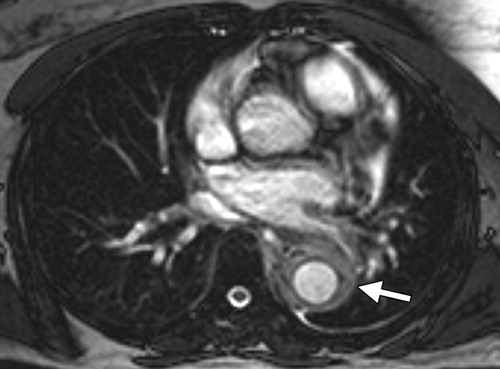
Radiographics Restrepo 2011
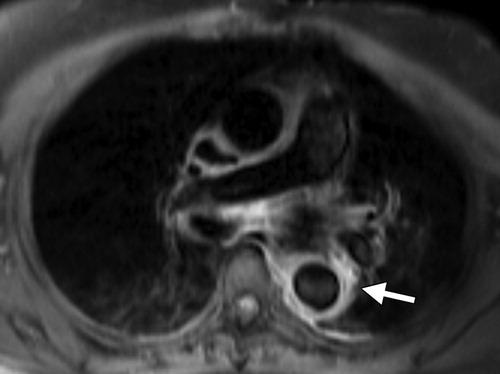
Radiographics Restrepo 2011
References
1- Restrepo et al Aortitis: Imaging Spectrum of the Infectious and Inflammatory Conditions of the Aorta, Radiographics
TCV