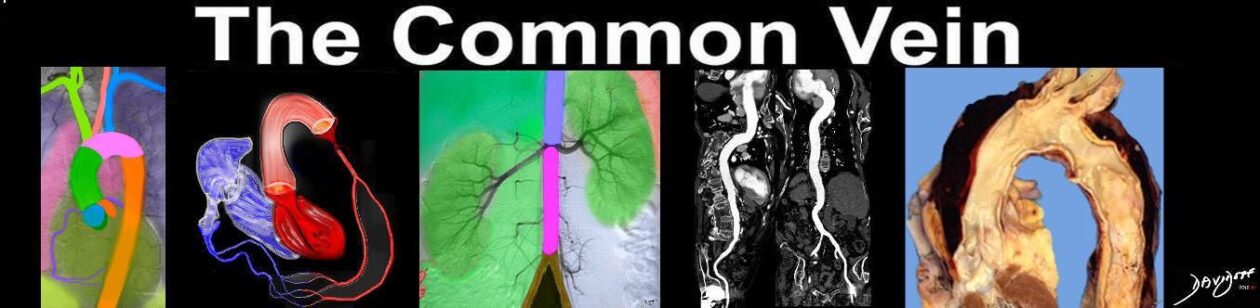
Isthmus
Copyright 2007
Ashley Davidoff MD
The isthmus is a slight constriction (approximately 3 mm) of the aorta just proximal to the point of attachment of the ductus arteriosus and distal to the origin of the left subclavian. It is characterized structurally by minimal narrowing of the tubular segment at that point. It serves as a marker for the site of the ductus arteriosus in fetal circulation and for the ligamentum arteriosum, a fibrous remnant in the child and adult. The narrowing of the aorta is simply the remnant of the embryologic structure. Common diseases at this include atherosclerosis, coarctation of the aorta and patent ductus arteriosus. Diagnostic studies include CT imaging, aortography, MRI and echocardiography. Surgical treatment is most common.
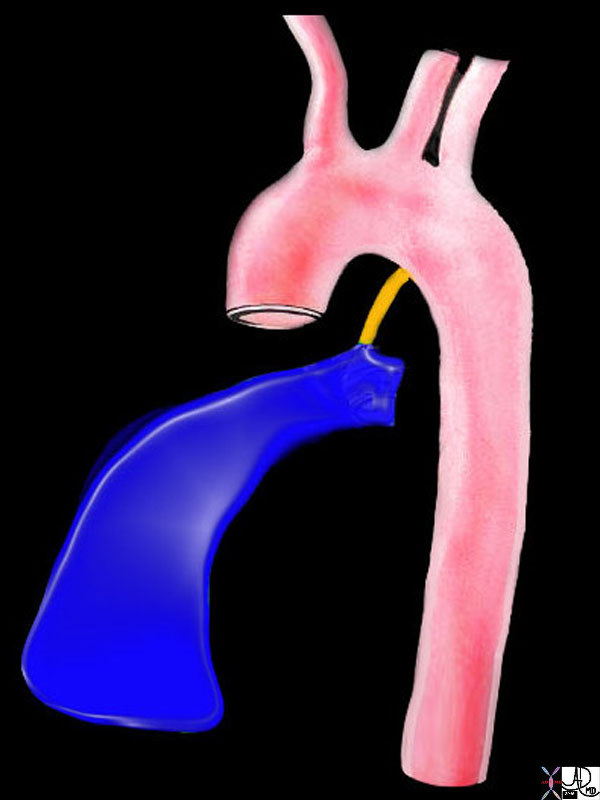
47680 right ventricle heart cardiac right ventricular outflow tract ligamentum arteriosum ductus arteriosus aorta isthmus Davidoff art Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net
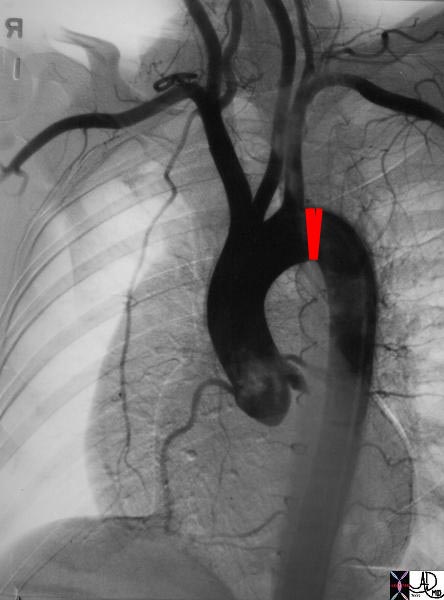
keywords aorta arch artery ascending descending normal thorax thoracic aorta ascending aortic valve sinus of Valsalva normal
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 35324b04
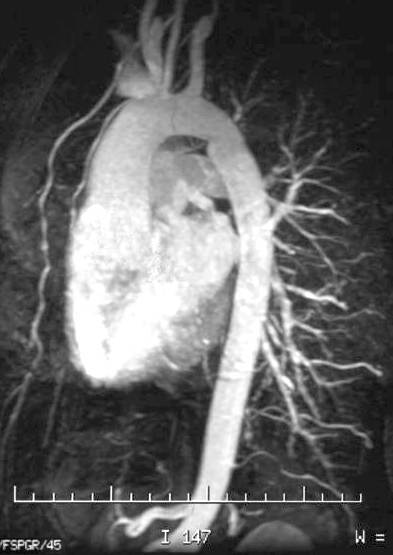
Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 27104b.jpg
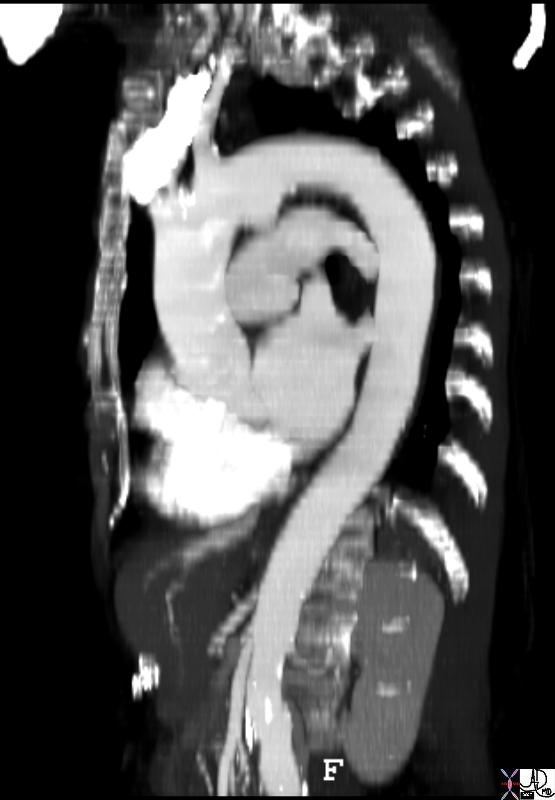
Ductus Diverticulum |
| 72871.800 aorta thorax abdomen arch ascending descending abdominal progressive and gradual size change ductus diverticulum normal anatomy CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
Applied Biology
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
PDA is a congenital persistence of an emryolog shunt – cause unknown sometimes in isolation sometimes in association with other congenital lesions results in left to right shuny increased blood flow to lungs relative decrease in flow to body with most clinical manifestations relating to increase fow Left untreated the iolated lesion will usuallyprogress to pulmonary hypertension and eventually Eisenmenger physiology meaning shunt goes right to left with subsequent cyanosis
dx echocardiography rx Non invasive chemical and surgical intervention are all options
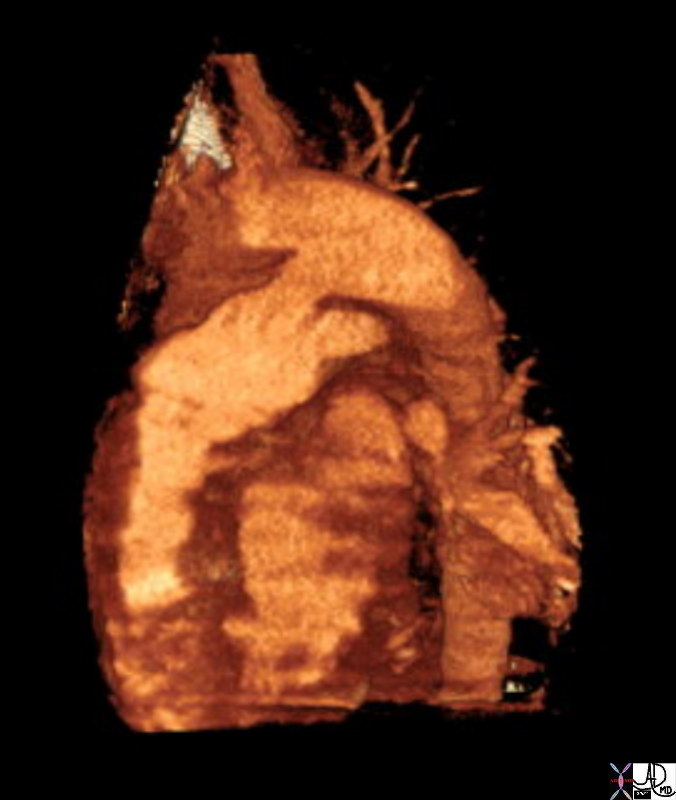
Patent Ductus Arteriosus |
| 42326.800 aorta pulmonary artery finding PDA patent ductus arteriosus left to right shunt arteriovenous malformation CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
Coarctatation of the Aorta
Congenital – may be in isolation part of the HLHS or in association with other congenital heart diseases dx imaging echo sometimes MRI rx Non invasive techniques and surgical
Few types – most common is at the level of the istmus
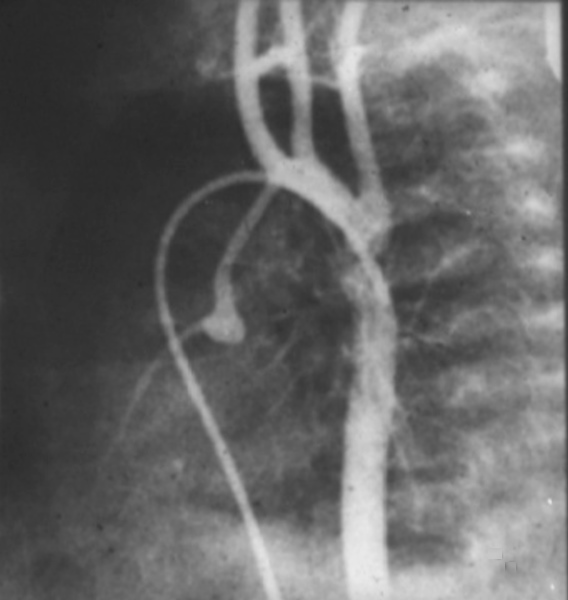
The catheter for tis angiogram was advanced from the femoral vein into the RA then to RV and then via a PDA into the aorta. Contrast injected into the descending aorta flowed retrograde into the ascending aorta since this was of low pressure die to the atretic aortic valve not being in communication with the systemic pressure of the LV. The coronaries are also filled in retrograde fashion. The ascending aorta is severely narrowed, the arch is hypoplastic and there is a coarctation. This is only part of the hypoplasia of the left system which more often than not involves varying degrees of atresia and hypoplasia of the LV and mitral apparatus.
keywords heart cardiac coronary artery aorta small dx aortic atresia tubular hypoplasia aortic coarctation aortic atresia PDA patent ductus arteriosus angiogram angiography CHD congenital heart disease Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 00269b02
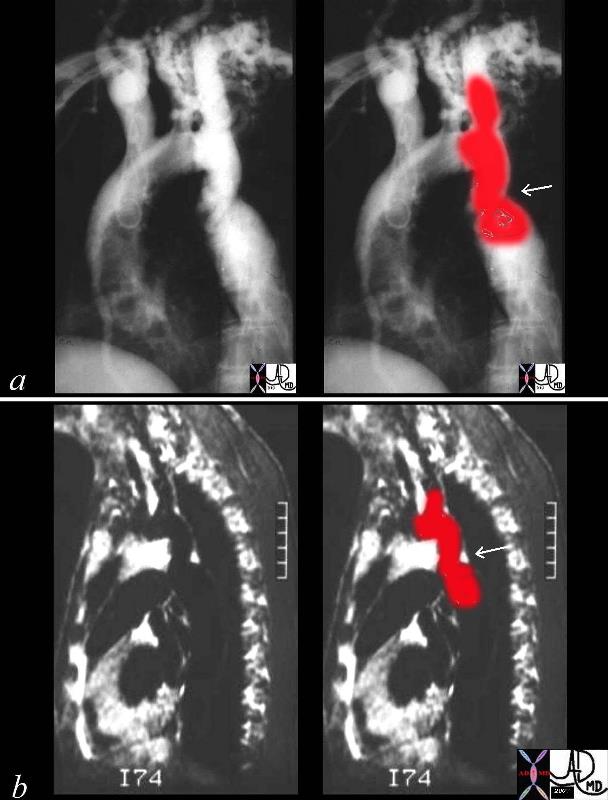
Coartcation of the Aorta |
| 00254c04 This combination of an angiogram and MRI show a focal coarctation of the aorta distal to the dilated left subclavian artery. Note the large internal mammary artery in the angiogram (a) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 00254c02 CVS aorta thorax thoracic aorta coarctation |
Aortic Interruption
Congenital – may be in isolation part of the HLHS or in association with other congenital heart diseases dx imaging echo sometimes MRI rx Non invasive techniques and surgical
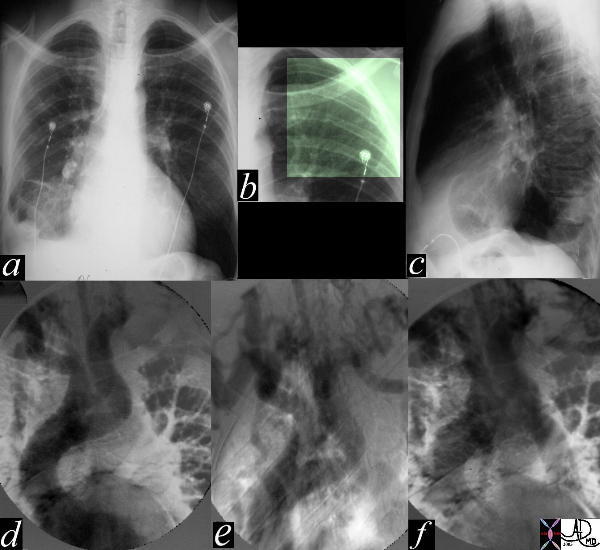
Aortic Interruption at the Level of the Isthmus |
| The most obvious finding in this CXR (a) with pleuro-parenchymal changes is not the most significant. In image (b) the highlighted ribs reveal rib notching characteristic of coarctation of the aorta. The lateral examination (c) in this instance is not helpful. In the early phase of the angiogram(d), there appears to be complete interruption of the aorta with a large left subclavian artery acting as a collateral pathway. The sbsequent images e, and f, show progressive filling of the isthmus and distal thoracic aorta. The coarcatation becomes apparent characterised by a “3” sign. 35107c Courtesy Laura Feldman MD code CVS artery aorta thorax coarctation rib notching bone collateral |
Aortic Trauma
Few types – most common is at the level of the isthmus
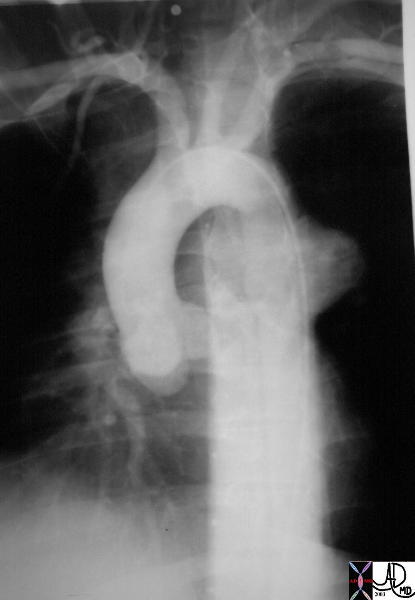
Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm at the Level of the Isthmus |
| 35260 Courtesy of Laura Feldman MD. code aneurysm aorta artery pseudoaneurysm thorax trauma traumatic anerusym |