Bulbous Portion of the Ascending Aorta
aka Sinuses of Valsalva
The Common Vein Copyright 2007
Introduction
Max Diameter in males 4cms and females 3.4cms
The sinuses of Valsalva are dilated cavities between the aortic leaflets and the ascending aortic wall. They are subdivided into the left, right and posterior sinuses. The sinuses are characterized structurally by their bulging shape protruding into the aortic wall. They act as a buffer between the leaflets, giving rise to the left and right coronary arteries at the sinotubular junction. They are not as commonly the source of disease but may rarely become aneurysmal. Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm is most easily diagnosed by echocardiography and requires surgical treatment.
The bulbous portion houses the aortic valves and the aortic annulus, and gives origin to the coronary arteries. These are the only set of branching vessels that arise from the ascending aorta. Each main coronary artery arises from its respective right and left coronary cusp. The non coronary cusp lies inferior and posterior to each of the coronary cusps. Behind each valve leaflet, is the pocket called the sinus of Valsalva. The sinuses become filled with blood during diastole causing the valves to coapt with each other and prevent backward flow into the LV. During systole the valve leaflets are forced open and the sinuses are functionally and virtually obliterated. The complex of valves and sinuses is called the bulb of the aorta, and its dimensions are just slightly larger than that of the ascending aorta itself.
Sinuses of Valsalva and Aortic Valve |
| 35324b03 thoracic aorta ascending aortic valve sinus of Valsalva normal Courtesy of Laura Feldman MD code aorta arch artery ascending descending normal thorax |
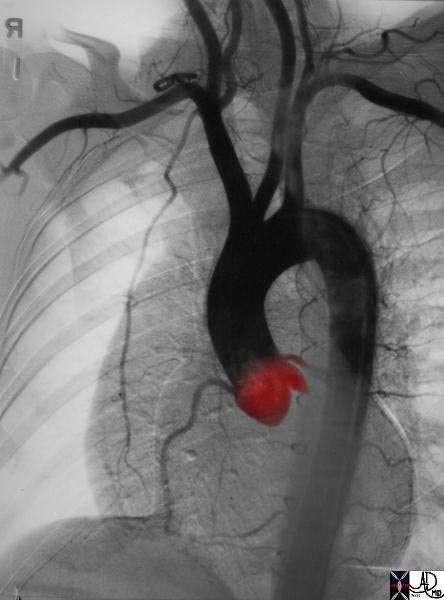
Aortic Valve and Sinuses |
| 07970 The aorta and the outflow components of the LV They demonstrate the makeup of the sinus (aka bulbous portion) of the aorta showing the aortic valveand the aortc sinus LVOT has been opened showing the three valve leaflets and their associated sinuses. between the right and non-coronay cusp, while the anterior and posterior branches are distributed in the septum (s). The right and left aortic cusps each contain a coronary ostium The non coronary cusp lies between the the left and right cusps, and is without an ostium. The anterior leaflet of the mitral valve participates as the lateral wall of the LVOT, and is attached to the non and left coronary cusp. Courtesy Ahley Davidoff MD code CVS normal aorta heart LV LVOT left bundle branch mebranous septum sinus of Valsalva left right coronary ostium AO AOV aortic valve commissure imaging radiology anatomy overlay anatomy normal |
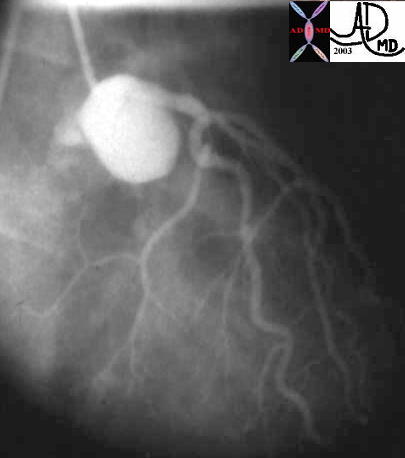
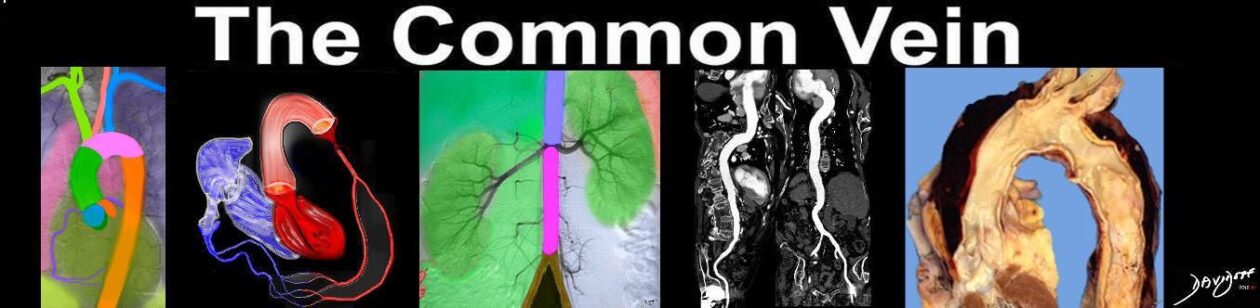
Reflux of Contrast into the Left Coronary Sinus of Valsalva with Injection of LAD |
| Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 07076 code heart artery coronary LAD circumflex obtuse marginal OM normal septal LM left main diagonal coronary ostium sinus valsalva imaging radiology angiography |
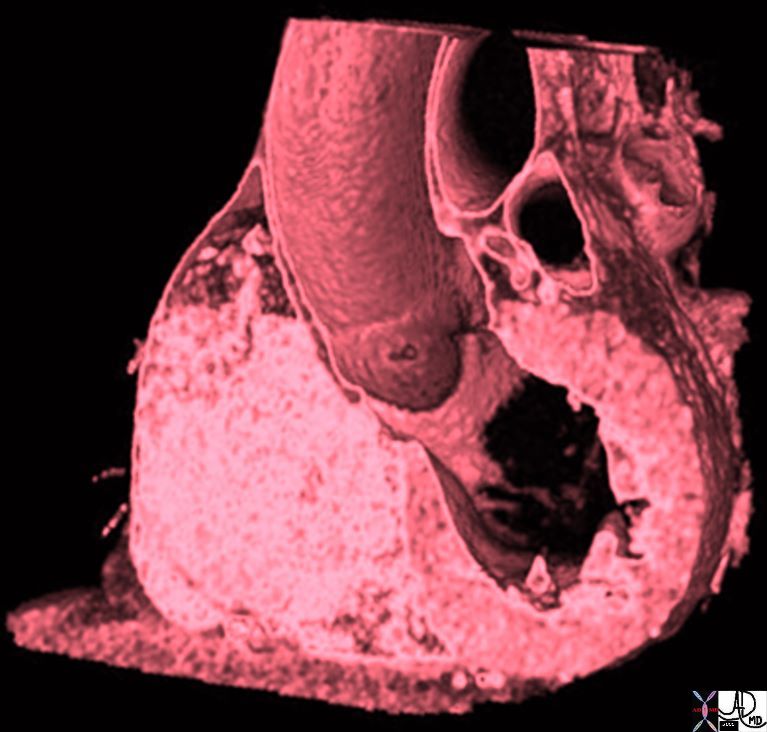
Aortic Bulb Sinotubular Junction, and Tubular Components of the Ascending Aorta |
| 47823 heart cardiac ascending aorta shape aortic tuck mitral valve to aortic fibrous continuity AV MV normal anatomy CTscan Davidoff MD |
Size
The diameter of the bulbous portion is up to 4cms.
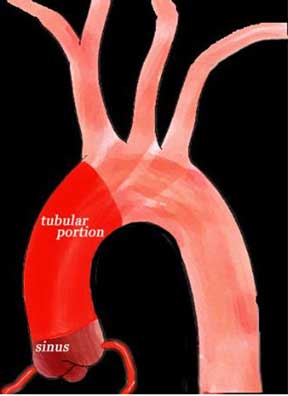
This diagram shows the two components of the ascending aorta, the bulbous or sinus portion (maroon) and the tubular portion (bright red) that starts at the sinotubular junction and ends at the origin of the brachiocephalic artery. Certain diseases such as syphilitic aortitis affect the tubular portion of the ascending aorta and spare the sinus portion, whereas others such as ankylosing spondylitis affect the aortic sinuses as well as the tubular portion.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net aorta Philips 011
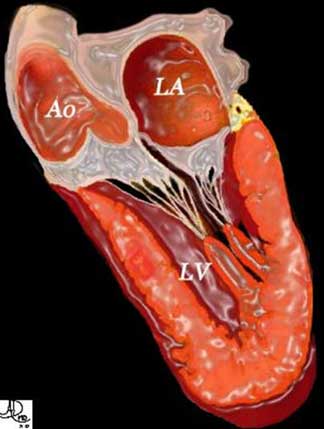
The ascending aorta originates from the left ventricle and together with its valve, is intimately attached to the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve. This diagram shows the relationship between the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, the aortic valve, and the bulbous portion of the ascending aorta.
Courtesy of: Ashley Davidoff, M.D.TheCommonVein.net Philips 013
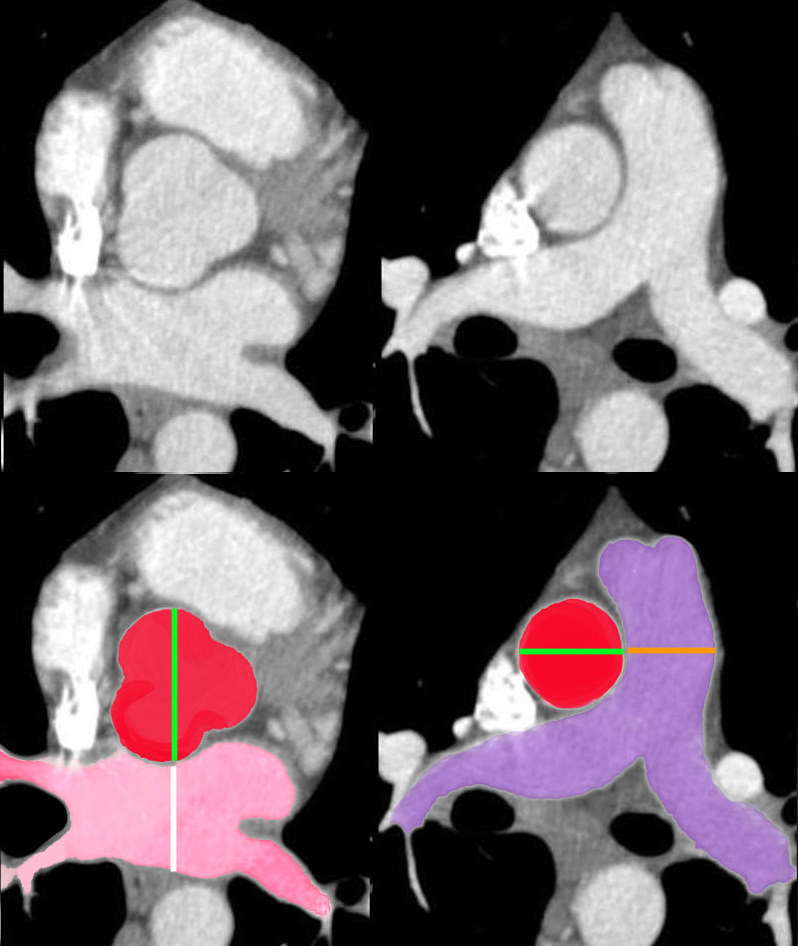
Aorta to Pulmonary Artery Ratio Sinus Portion and Tubular Portion |
| 34769c07b02 heart cardiac aortic valve pulmonary valve conus infundibulum RVOT right ventricular outflow tract pulmonary artery normal size aorta to PA ratio aorta to LA ratio anatomy CTscan Davidoff MD |
Shape
The bulbous portion as its name implies is bulbous in shape.
Position
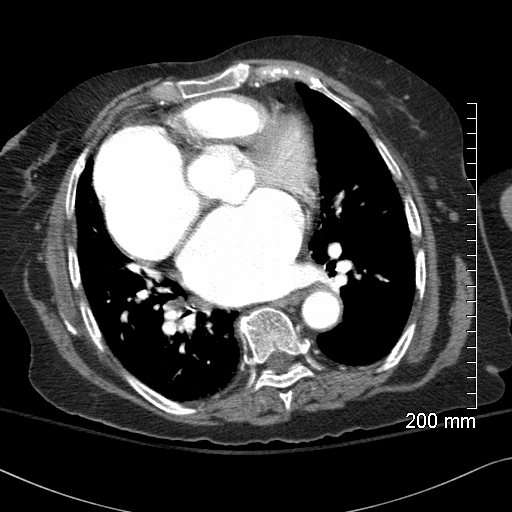
The aortic sinus lies in one of the most comfortable spots in the body. On its right cusp it is cushioned by the right atrium and its non coronary cusp is cushioned by the left atrium
keywords heart cardiac aorta right atrium RAE left atrium LAE fx enlarged aorta finding normal fx aorta lies between the cushions of the LA and RA most comfortable spot in the body dx CHF CTscan
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 48079
The aortic sinus lies in one of the most comfortable spots in the body. On its right cusp it is cushioned by the right atrium and its non coronary cusp is cushioned by the left atrium.
Applied Biology
Annulo-aortic Ectasia (aka Sinotubular Ectasia)
Annulo-aortic ectasia is marked by severe degenerative changes in the wall of the aorta resulting in idiopathic dilation of the proximal aorta and aortic annulus
Statistics
5-10% of patients undergoing aortic valve replacement for pure aortic regurgitation have annulo-aortic ectasia.
Causative Factors
Probably due to abnormalities in collagen cross-linking or elastic tissue Classic Marfan syndrome Some overlying features of Marfan M:F 2-8:1 4th to 6th decade
Diagnosis
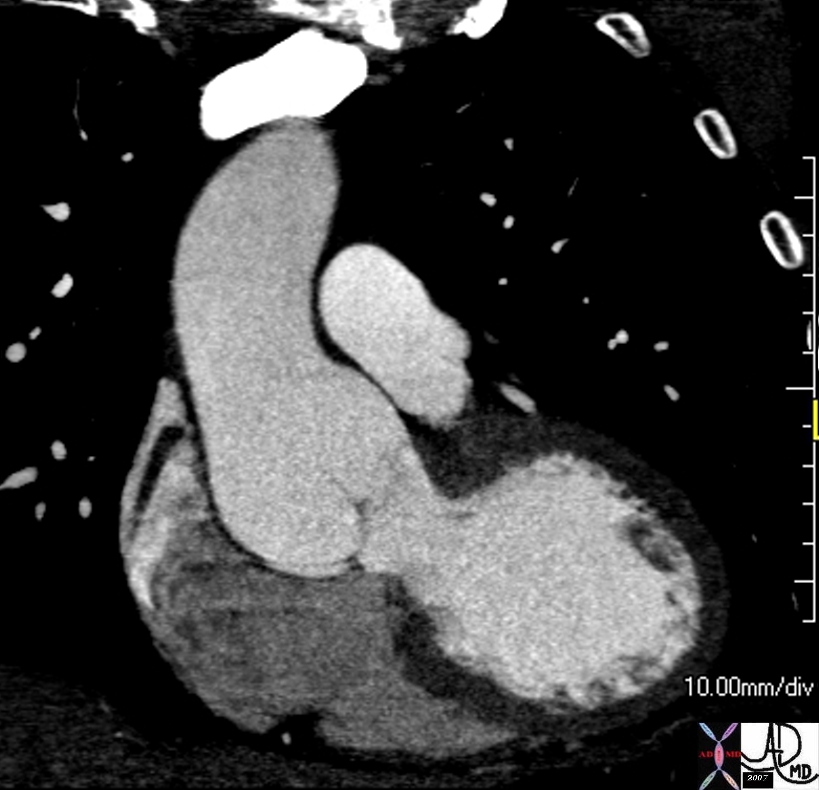
Sinotubular Ectasia – Marfan’s Syndrome |
| In this case the transverse diameter of the sinuses measured 5.3cms
keywords thoracic aorta sinus of Valsalva aortic sinuses sinotubular junction of ascending aorta sinotubular ectasia fx dilated CTscan Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 72712 |
Clinical
Marfan’s syndrome or Marfanoid features May have features of aortic regurgitation or acute aortic dissection RX Surgical correction involves replacement of the aortic valve and resection of the aneurysmal aorta with reimplantation of the coronary arteries
Aneurysm of Sinus of Valsalva
Size and shape disorder associated with Marfans, Ehlos Danlos…. results. may prolapse AR dx echo and CT Rx Surgical when indicated
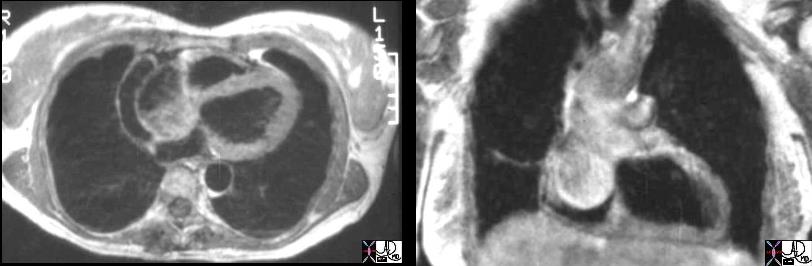
Marfan’s Syndrome Sinus of Valsalva Aneurysm |
| 07974c01 heart cardiac right atrium aortic valve aortic sinus fx right atrial filling defect dx sinus of Valsalva aneurysm of the right aortic sinus prolapsing into the right atrium (RA defect) dx Marfan’s Syndrome MRI T1 weighted Davidoff MD 07973.800 07974c01 07974.800 |
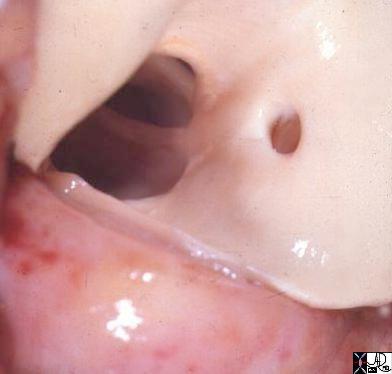
Congenitally Small Sinuses Bicuspid Aortic Valve and Malposition of Coronary Ostium |
| 15049 aorta aortic valve bicuspid aortic valve hypoplastic valve anomalous positioning of a coronary ostium coronary artery congenital abnormality position goss pathology Davidoff MD |
Disease at the Sinotubular Junction
Supravalvar Aortic Stenosis – William’s Syndrome
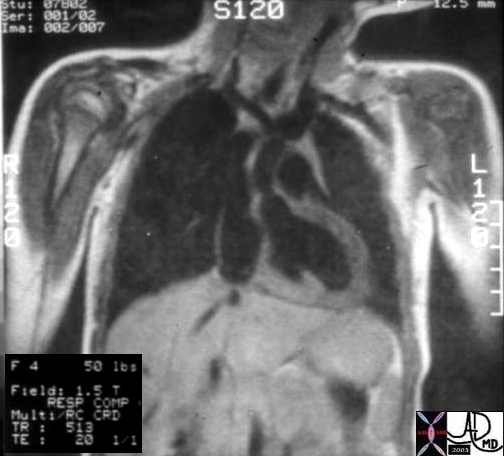
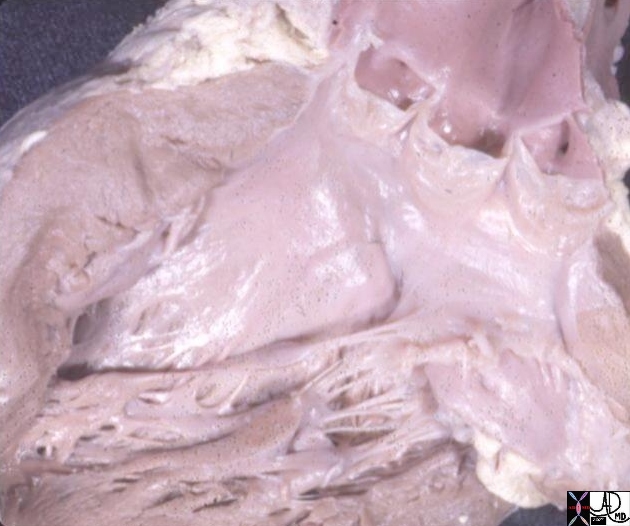
Supravalvar Aortic Stenosis |
| Hx 4 year female with cocktail personality and Williams Syndrome showing supravalvar aortic stenosis
keywords heart cardiac artery aorta supravalvular aortic stenosis supravalvar aortic stenosis Williams syndrome William’s syndrome Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net 08233b01 |