| Imaging
The Common Vein Copyright 2007
Indications
Congenital – aortic coarctation, marfan syndrome
Trauma – pseudoaneurysm, transection
Acute aortic syndromes – aortic dissection, intramural hematoma, penetrating ulcer
Aneurysms – surveillance, pre-operative planning, followup after repair, rupture, mycotic
Atherosclerosis – aortic stenosis
Aortitis – Takayasu’s
Advantages
Ultrasound
– Fast
– available
– inexpensive
– non-ionizing radiation
CT
– fast, can image acutely ill patients
– available
MRI
– non-ionizing radiation
Catheter Angiography
– interventions: angioplasty, stenting
Disadvantages
Ultrasound
– operator dependent
– limited indications
CT
– ionizing radiation
– iodinated contrast material
MRI
– cannot scan unstable patients
Catheter Angiography
– invasive
– ionizing radiation
– iodinated contrast material
Method
Patient preparation none
Equipment
Ultrasound
CT
MRI
Catheter angiography
Technique
CTA
Non-contrast followed by contrast injection bolus timing
Gated if evaluating aortic root, ascending aortic aneurysm or cardiac evaluation
MRI/MRA
Thoracic aorta
Torso phased array coil, gadolinium 0.1 to 0.2 mmol/kg (20 – 30 mL)
Double inversion recovery fast spin echo
Cine gradient echo
Test bolus
Post-contrast 3D MRA, 2 to 3 mL/s, arterial and venous phases
Abdominal aorta
Torso phased array coil, gadolinium 0.1 to 0.2 mmol/kg (20 – 30 mL)
T1 gradient echo
Test bolus
Post contrast 3D MRA, 2 to 3 mL/s, arterial and venous phases
Results
Acute aortic dissection by MDCT1
Sensitivity 99%
Specificity 100%
PPV 100%
NPV 99.7%
Accuracy 99.5%
Thoracic aortic dissections by MRI2
Sensitivity 98.3%
Specificity 97.8%
Traumatic aortic rupture
Sensitivity 100%
Specificity 81.%
Intramural Hematoma, diagnostic accuracy by CT
Sensitivity 82%
Specificity 100%
Accuracy 84%
References
1. Hayter RG, Rhea JT, Small A, Tafazoli FS, Novelline RA. Suspected Aortic Dissection and Other Aortic Disorders: Multi-Detector Row CT in 373 Cases in the Emergency Setting. Radiology 2006; 238:841-852.
2. Nienaber CA, von Kodolitsch Y, Nicols V, Siglow V, Piepho A, Brockhoff C, Koschyk DH, Spielmann RP. The Diagnosis of Thoracic Aortic Dissection by Noninvasive Imaging Procedures. NEJM 1993; 328:1-9.
3. Gavant ML, Menke PG, Fabian T, Flick PA, Graney MJ, Gold RE. Blunt Traumatic Aortic Rupture: Detection with Helical CT of the Chest. Radiology 1995; 197: 125-133.
4. Yoshida S, Akiba H, Tamakawa M, Yama N, Hareyama M, Morishita K, Abe T. Thoracic Involvement of Type A Aortic Dissection and Intramural Hematoma: Diagnostic Accuracy – comparison of Emergency Helical CT and Surgical Findings. Radiology 2003; 2
| Imaging
The Common Vein Copyright 2007
Indications
Congenital – aortic coarctation, marfan syndrome
Trauma – pseudoaneurysm, transection
Acute aortic syndromes – aortic dissection, intramural hematoma, penetrating ulcer
Aneurysms – surveillance, pre-operative planning, followup after repair, rupture, mycotic
Atherosclerosis – aortic stenosis
Aortitis – Takayasu’s
Advantages
Ultrasound
– Fast
– available
– inexpensive
– non-ionizing radiation
CT
– fast, can image acutely ill patients
– available
MRI
– non-ionizing radiation
Catheter Angiography
– interventions: angioplasty, stenting
Disadvantages
Ultrasound
– operator dependent
– limited indications
CT
– ionizing radiation
– iodinated contrast material
MRI
– cannot scan unstable patients
Catheter Angiography
– invasive
– ionizing radiation
– iodinated contrast material
Method
Patient preparation none
Equipment
Ultrasound
CT
MRI
Catheter angiography
Technique
CTA
Non-contrast followed by contrast injection bolus timing
Gated if evaluating aortic root, ascending aortic aneurysm or cardiac evaluation
MRI/MRA
Thoracic aorta
Torso phased array coil, gadolinium 0.1 to 0.2 mmol/kg (20 – 30 mL)
Double inversion recovery fast spin echo
Cine gradient echo
Test bolus
Post-contrast 3D MRA, 2 to 3 mL/s, arterial and venous phases
Abdominal aorta
Torso phased array coil, gadolinium 0.1 to 0.2 mmol/kg (20 – 30 mL)
T1 gradient echo
Test bolus
Post contrast 3D MRA, 2 to 3 mL/s, arterial and venous phases
Results
Acute aortic dissection by MDCT1
Sensitivity 99%
Specificity 100%
PPV 100%
NPV 99.7%
Accuracy 99.5%
Thoracic aortic dissections by MRI2
Sensitivity 98.3%
Specificity 97.8%
Traumatic aortic rupture
Sensitivity 100%
Specificity 81.%
Intramural Hematoma, diagnostic accuracy by CT
Sensitivity 82%
Specificity 100%
Accuracy 84%
References
- Hayter RG, Rhea JT, Small A, Tafazoli FS, Novelline RA. Suspected Aortic Dissection and Other Aortic Disorders: Multi-Detector Row CT in 373 Cases in the Emergency Setting. Radiology 2006; 238:841-852.
- Nienaber CA, von Kodolitsch Y, Nicols V, Siglow V, Piepho A, Brockhoff C, Koschyk DH, Spielmann RP. The Diagnosis of Thoracic Aortic Dissection by Noninvasive Imaging Procedures. NEJM 1993; 328:1-9.
- Gavant ML, Menke PG, Fabian T, Flick PA, Graney MJ, Gold RE. Blunt Traumatic Aortic Rupture: Detection with Helical CT of the Chest. Radiology 1995; 197: 125-133.
- Yoshida S, Akiba H, Tamakawa M, Yama N, Hareyama M, Morishita K, Abe T. Thoracic Involvement of Type A Aortic Dissection and Intramural Hematoma: Diagnostic Accuracy – comparison of Emergency Helical CT and Surgical Findings. Radiology 2003; 2
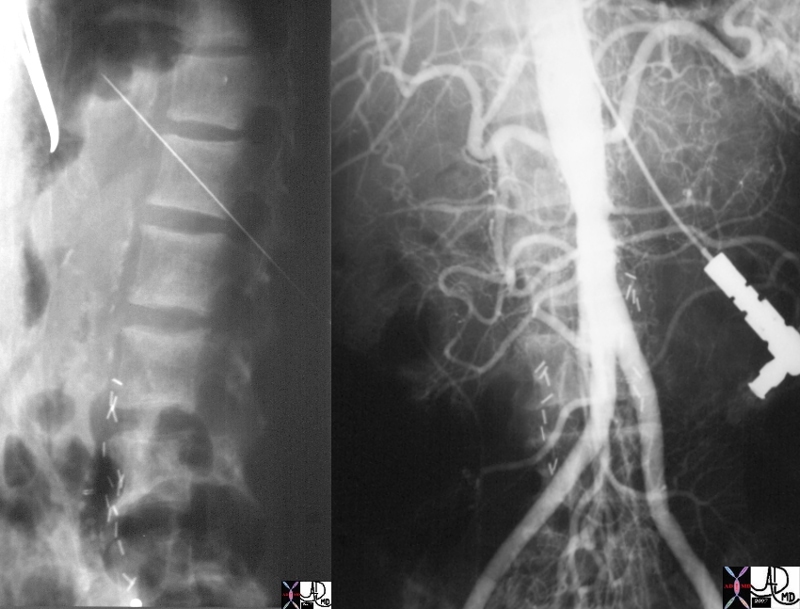 Translumbar Aortography Translumbar Aortography |
| 22776c01 aorta kidney renal artery stenosis occlusion bone spine v |
Translumbar Aortography |
| 22776c01 aorta kidney renal artery stenosis occlusion bone spine vertebra fx sclerosis of the endplates sign rugger jersey spine dx chronic renal failure translumbar aortography TLA angiography Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
|
 Translumbar Aortography
Translumbar Aortography