|
Congenital Diseases of the Aorta
The Common Vein Copyright 2007
Ashley Davidoff MD
|
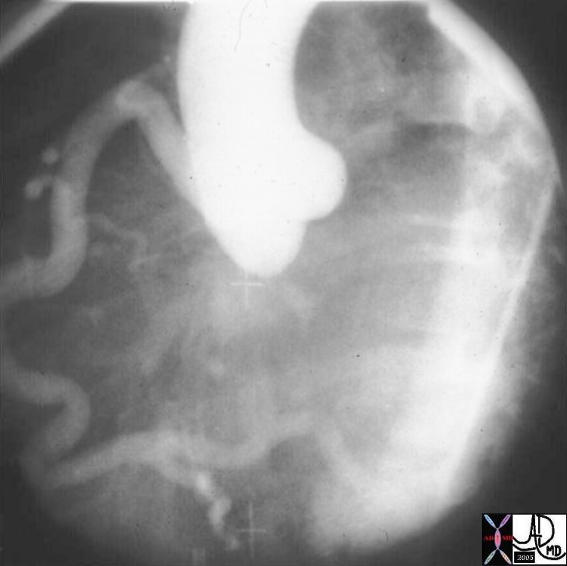 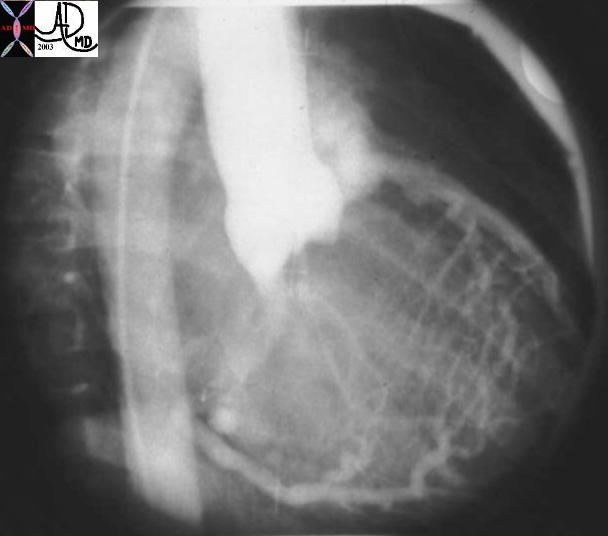 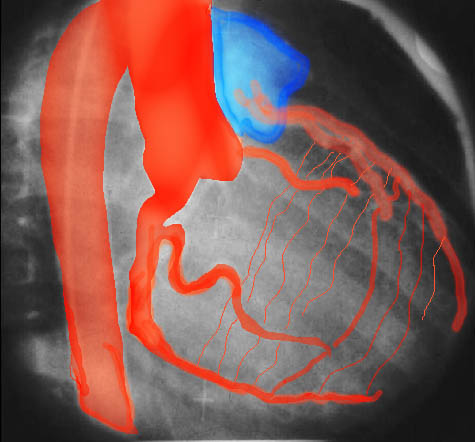
Anomalous Origin of the Coronary Artery from the MPA
|
| This injection into the base of the aorta showing filling of a dilated right coronary artery, collateral flow through the septal perforators, into a dilated LAD and then into the main pulmonary artery. (MPA) This is a case of anomalous origin of the left coronary from the MPA. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 07024 code cardiac heart artery coronary LAD circumflex anomalous origin of LAD from MPA congenital septal artery collateral large AVM imaging radiology angiography
07024 15038 15038c01 cardiac heart coronary artery RCA enlarged enlarged septal collaterals retrograde filling of LAD aberrant anomalous origin of the LAD from MPA angiogram angiography Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
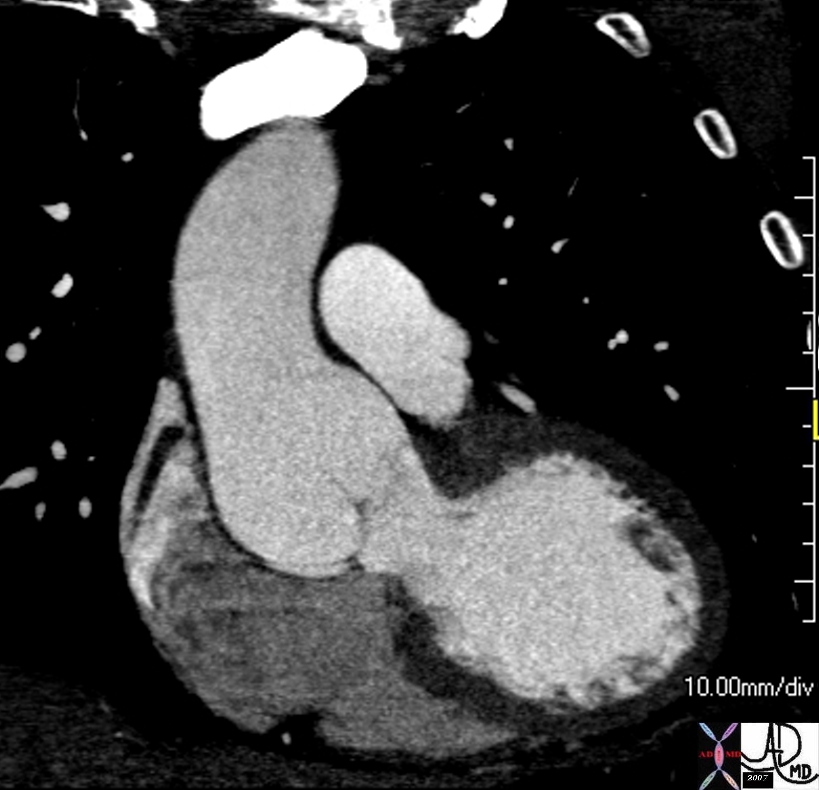
Sinotubular Ectasia
|
| 72712 thoracic aorta sinus of Valsalva aortic sinuses sinotubular junction of ascending aorta sinotubular ectasia fx dilated CTscan Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD 72709 |
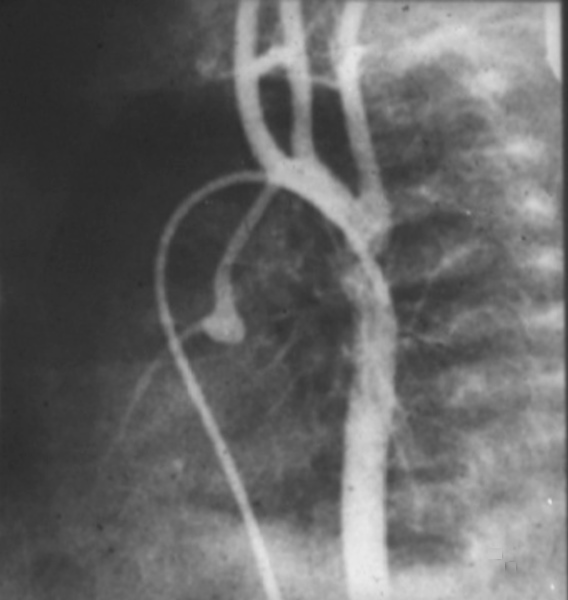
Aortic Valve Atresia in the Setting of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
|
| 00269b02 heart cardiac coronary artery aorta small dx aortic atresia tubular hypoplasia aortic coarctation aortic atresia PDA patent ductus arteriosus angiogram angiogaphy CHD |
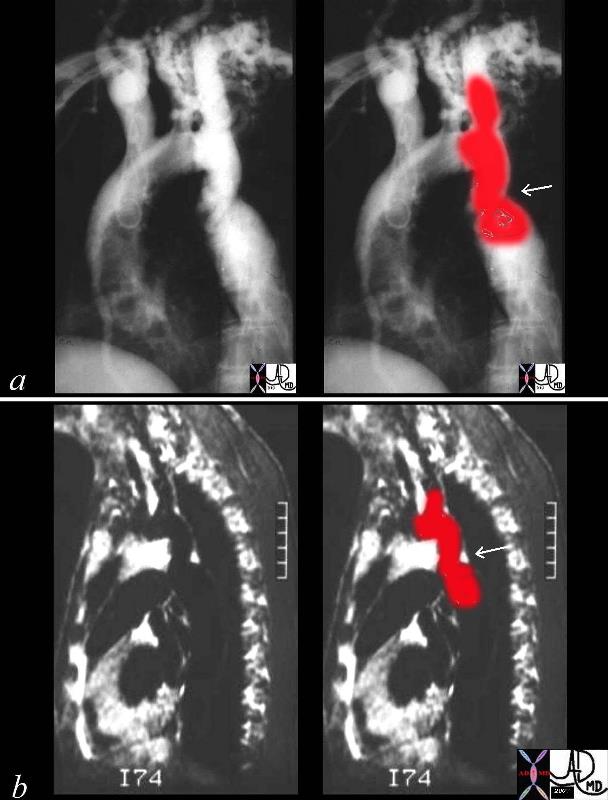
Coartcation of the Aorta
|
| 00254c04 This combination of an angiogram and MRI show a focal coarctation of the aorta distal to the dilated left subclavian artery. Note the large internal mammary artery in the angiogram (a) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 00254c02 CVS aorta thorax thoracic aorta coarctation |
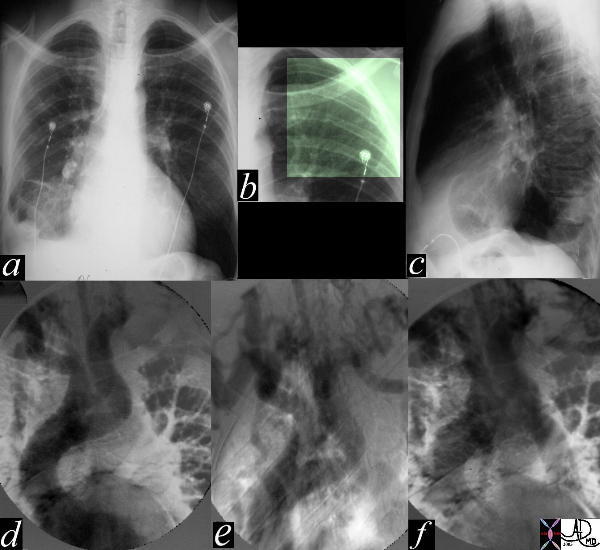
Aortic Interruption at the Level of the Isthmus
|
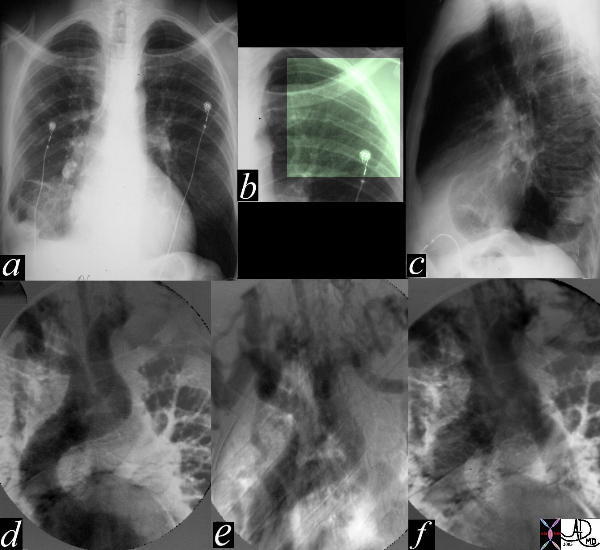
| The most obvious finding in this CXR (a) with pleuro-parenchymal changes is not the most significant. In image (b) the highlighted ribs reveal rib notching characteristic of coarctation of the aorta. The lateral examination (c) in this instance is not helpful. In the early phase of the angiogram(d), there appears to be complete interruption of the aorta with a large left subclavian artery acting as a collateral pathway. The sbsequent images e, and f, show progressive filling of the isthmus and distal thoracic aorta. The coarcatation becomes apparent characterised by a “3” sign. 35107c Courtesy Laura Feldman MD code CVS artery aorta thorax coarctation rib notching bone collateral |
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
|
| 42326.800 aorta pulmonary artery finding PDA patent ductus arteriosus left to right shunt arteriovenous malformation CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
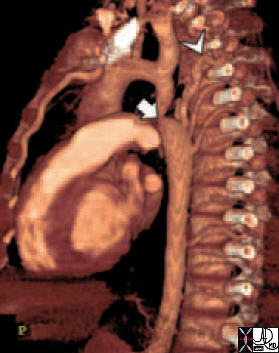
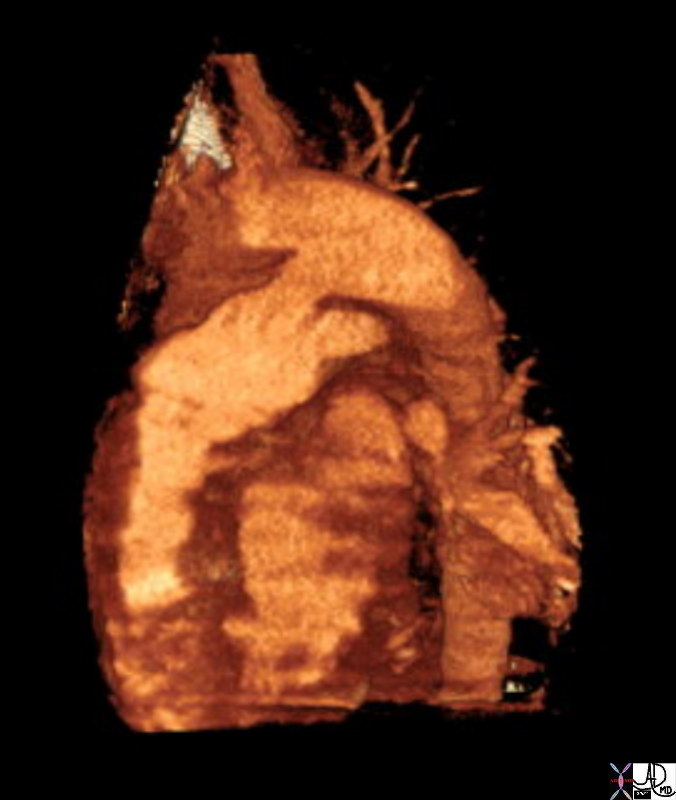
Coartctation – Reconstruction |
| 44146 coarctation of the aorta heart cardiac CTscan MDCT Courtesy Philips Medical |
Coarctation |
| The most obvious finding in this CXR (a) with pleuro-parenchymal changes is not the most significant. In image (b) the highlighted ribs reveal rib notching characteristic of coarctation of the aorta. The lateral examination (c) in this instance is not helpful. In the early phase of the angiogram(d), there appears to be complete interruption of the aorta with a large left subclavian artery acting as a collateral pathway. The sbsequent images e, and f, show progressive filling of the isthmus and distal thoracic aorta. The coarcatation becomes apparent characterised by a “3” sign. 35107c Courtesy Laura Feldman MD code CVS artery aorta thorax coarctation rib notching bone collateral |
|